Dynamically derived morphology from the recurrence patterns of close binary stars using Kepler data
Dynamically derived morphology from the recurrence patterns of close binary stars using Kepler data
Anisha R. V. Kashyap, D. Pawar, R. Misra, G. Ambika, Sandip V George
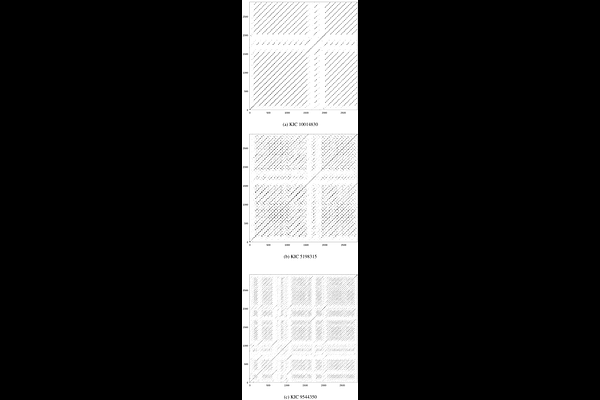
AbstractIn this work, we propose a novel method to classify close binary stars, derived from the dynamical structure inherent in their light curves. We apply the technique to light curves of binaries from the revised Kepler Eclipsing binary catalog, selecting close binaries which have the standard morphology parameter, $c$, $\gt 0.5$ corresponding to semi-detached, over-contact and ellipsoidal systems. Using the method of time delay embedding, we recreate the non-linear dynamics underlying the data and quantify the patterns of recurrences in them. Using two recurrence measures, Determinism and Entropy, we define a new Dynamically Derived Morphology (DDM) parameter and compute its values for the Kepler objects. While as expected, this metric is somewhat inversely correlated with the existing morphology parameter (Spearman $\rho= -0.32$), the method offers an alternate classification scheme for close binary stars that captures their nonlinear dynamics, an aspect often overlooked in conventional methods. Hence, the DDM parameter is expected to distinguish between stars with similar folded light curves, but are dynamically dissimilar due to nonlinear effects. Moreover, since the method can be easily automated and is computationally efficient it can be effectively used for future sensitive large data sets.