Core-collapse supernova parameter estimation with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory
Core-collapse supernova parameter estimation with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory
Andrea Simongini, F. Ragosta, I. Di Palma, S. Piranomonte
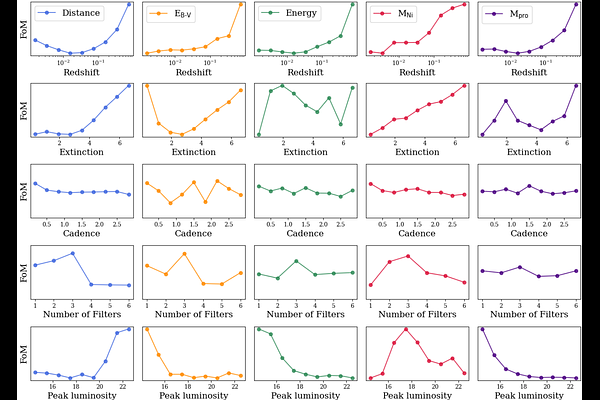
AbstractThe Vera Rubin Observatory's Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) is expected to revolutionize time-domain optical astronomy as we know it. With its unprecedented depth, the LSST will survey the southern hemisphere sky, generating nearly 32 trillion observations over its nominal 10-year operation. Among these, approximately 10 million will be supernovae (SNe). These observations will uniquely characterize the SN population, enabling studies of known and rare SN types, detailed parameterization of their light curves, deep searches for new SN progenitor populations, the discovery of strongly lensed SNe, and the compilation of a large, well-characterized sample of superluminous SNe. We analyzed a sample of 22663 simulations of LSST light curves for core collapse SNe (CCSNe), modeled using the radiative transfer code STELLA. We analyzed this dataset with the software CASTOR, which enables the reconstruction of synthetic light curves and spectra via a machine learning technique that allows one to retrieve the complete parameter map of a SN. For each parameter we compared the observed and the true values, determining how LSST light curves alone will contribute to characterize the progenitor and the explosion. Our results indicate that LSST alone will not suffice for a comprehensive and precise characterization of progenitor properties and explosion parameters. The limited spectral coverage of LSST light curves (in most cases) does not allow for the accurate estimation of bolometric luminosity, and consequently, of the explosion energy and nickel yield. Additionally, the redshift-absorption degeneracy is difficult to resolve without supplementary information. These findings suggest that for the most interesting SNe, complementary follow-up observations using spectrographs and optical facilities (particularly in the infrared bands) will be essential for accurate parameter determination.