Application of a modified commercial laser mass spectrometer as a science analog of the Mars Organic Molecule Analyzer (MOMA)
Application of a modified commercial laser mass spectrometer as a science analog of the Mars Organic Molecule Analyzer (MOMA)
Zachary K. Garvin, Anaïs Roussel, Luoth Chou, Marco E. Castillo, Xiang Li, William B. Brinckerhoff, Sarah Stewart Johnson
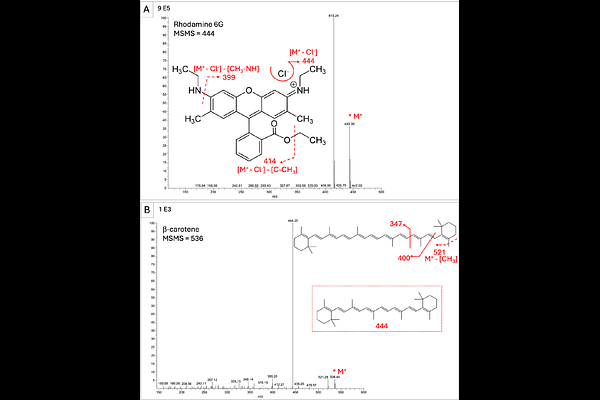
AbstractThe ESA/NASA Rosalind Franklin rover, planned for launch in 2028, will carry the first laser desorption ionization mass spectrometer (LDI-MS) to Mars as part of the Mars Organic Molecule Analyzer (MOMA) instrument. MOMA will contribute to the astrobiology goals of the mission through the analysis of potential organic biosignatures. Due to the minimal availability of comparable equipment, laboratory analyses using similar techniques and instrumentation have been limited. In this study, we present a modified commercial benchtop LDI-MS designed to replicate MOMA functionality and to enable rapid testing of samples for MOMA validation experiments. We demonstrate that our instrument can detect organic standards in mineral matrices, with MS/MS enabling structural identification even in complex mixtures. Performance was additionally validated against an existing LDI-MS prototype through the comparison of spectra derived from natural samples from a Mars analog site in the Atacama Desert. Lastly, analysis of Mars analog synthetic mineral mixes highlights the capacity of the instrument to characterize both the mineralogical and organic signals in mission-relevant samples. This modified benchtop instrument will serve as a platform for collaborative research to prepare for MOMA operations, test LDI parameters, and generate pre-flight reference data in support of the mission science and astrobiology specific goals.