Correlated reaction coordinate motion produces non-additive rate enhancement for electron and energy transfer in multi-acceptor structures
Correlated reaction coordinate motion produces non-additive rate enhancement for electron and energy transfer in multi-acceptor structures
Hanggai Nuomin, Feng-Feng Song, Peng Zhang, David N. Beratan
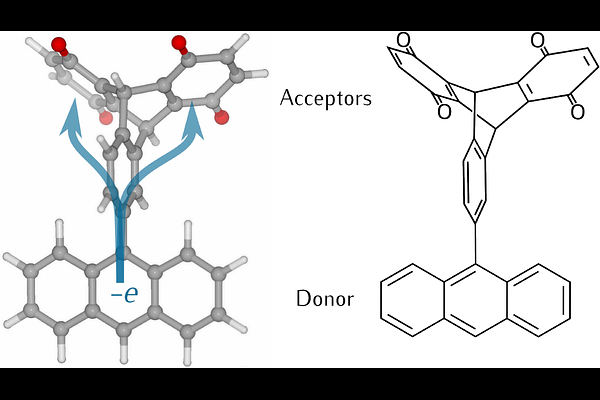
AbstractMolecular structures with multiple donor, bridge, or acceptor units can display quantum interference effects that influence electron and energy transfer (ET and EnT) rates. Recent experiments found a 4- to 5-fold increase in ET rates for donor-acceptor structures with two acceptors compared to one. This result is surprising: simple classical or quantum analysis suggests a factor of two rate enhancement. We analyze the coupling interactions in multiple acceptor systems and find that rate enhancements beyond additive effects arise from acceptor-acceptor interactions that: 1) shift the reaction free energy, 2) change the donor-acceptor couplings, and 3) alter the reaction-coordinate motion. Consideration of these effects explains the observed rates in multi-acceptor systems and suggests strategies to tailor energy and electron transfer kinetics.