COSMOS Web: Morphological quenching and size-mass evolution of brightest group galaxies from z = 3.7
COSMOS Web: Morphological quenching and size-mass evolution of brightest group galaxies from z = 3.7
Ghassem Gozaliasl, Lilan Yang, Jeyhan Kartaltepe, Greta Toni, Fatemeh Abedini, Hollis Akins, Natalie Allen, Rafael Arango-Toro, Arif Babul, Caitlin Casey, Nima Chartab, Nicole Drakos, Andreas Faisst, Alexis Finoguenov, Carter Flayhart, Maximilien Franco, Gavin Leroy, Santosh Harish, Günther Hasinger, Hossein Hatamnia, Olivier Ilbert, Shuowen Jin, Darshan Kakkad, Atousa Kalantari, Ali Ahmad Khostovan, Anton Koekemoer, Maarit Korpi-Lagg, Clotilde Laigle, Daizhong Liu, Georgios Magdis, Matteo Maturi, Henry Joy McCracken, Jed McKinney, Nicolas McMahon, Bahram Mobasher, Lauro Moscardini, Jason Rhodes, Brant Robertson, Louise Paquereau, Annagrazia Puglisi, Rasha Samir, Mark Sargent, Zahra Sattari, Diana Scognamiglio, Nick Scoville, Marko Shuntov, David Sanders, Sina Taamoli, Sune Toft, Eleni Vardoulaki
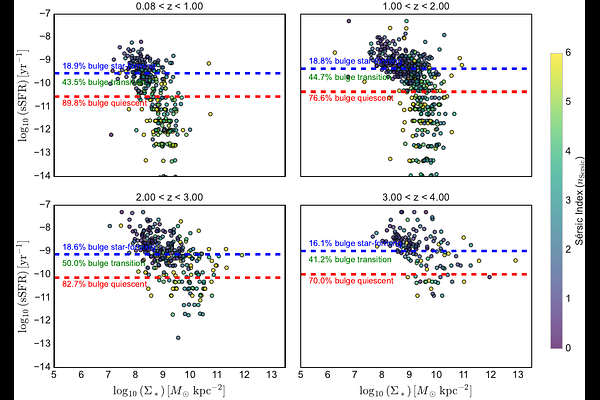
AbstractWe present a comprehensive study of the structural evolution of Brightest Group Galaxies (BGGs) from redshift $z \simeq 0.08$ to $z = 3.7$ using the \textit{James Webb Space Telescope}'s 255h COSMOS-Web program. This survey provides deep NIRCam imaging in four filters (F115W, F150W, F277W, F444W) across $\sim 0.54~\mathrm{deg}^2$ and MIRI coverage in $\sim 0.2~\mathrm{deg}^2$ of the COSMOS field. High-resolution NIRCam imaging enables robust size and morphological measurements, while multiwavelength photometry yields stellar masses, SFRs, and S\'ersic parameters. We classify BGGs as star-forming and quiescent using both rest-frame NUV--$r$--$J$ colors and a redshift-dependent specific star formation rate (sSFR) threshold. Our analysis reveals: (1) quiescent BGGs are systematically more compact than their star-forming counterparts and exhibit steeper size--mass slopes; (2) effective radii evolve as $R_e \propto (1+z)^{-\alpha}$, with $\alpha = 1.11 \pm 0.07$ (star-forming) and $1.40 \pm 0.09$ (quiescent); (3) star formation surface density ($\Sigma_{\mathrm{SFR}}$) increases with redshift and shows stronger evolution for massive BGGs ($\log_{10}(M_\ast/M_\odot) \geq 10.75$); (4) in the $\Sigma_*$--sSFR plane, a structural transition marks the quenching process, with bulge-dominated systems comprising over 80\% of the quiescent population. These results highlight the co-evolution of structure and star formation in BGGs, shaped by both internal and environmental processes, and establish BGGs as critical laboratories for studying the baryonic assembly and morphological transformation of central galaxies in group-scale halos.