SCUBADive II: Searching for $z>4$ Dust-Obscured Galaxies via F150W-Dropouts in COSMOS-Web
SCUBADive II: Searching for $z>4$ Dust-Obscured Galaxies via F150W-Dropouts in COSMOS-Web
Sinclaire M. Manning, Jed McKinney, Katherine E. Whitaker, Arianna S. Long, Olivia R. Cooper, Jaclyn B. Champagne, Nicole E. Drakos, Andreas L. Faisst, Maximilien Franco, Christopher C. Hayward, Michaela Hirschmann, Georgios E. Magdis, Margherita Talia, Francesco Valentino, John R. Weaver
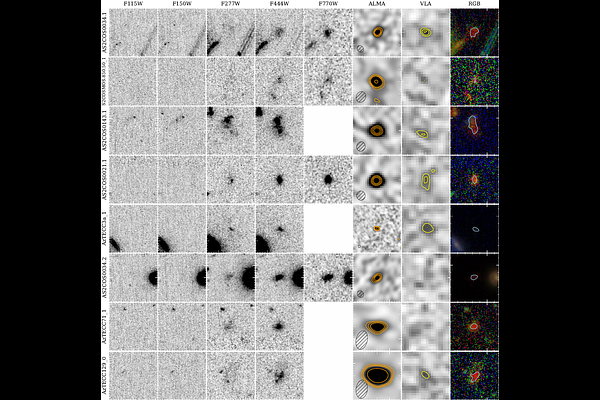
AbstractThe role of dust in the cosmic star formation budget remains highly uncertain, especially at $z>4$, where accurate bookkeeping of the dust-obscured component proves difficult. We address this shortcoming with SCUBADive, a compilation of the \jwst\ counterparts of (sub-)millimeter galaxies, in order to further analyze the distribution and properties of massive dust-obscured galaxies at early times. In this paper, we present a subset of SCUBADive, focusing on 60 ``dark'' galaxies that dropout at 1.5\micron. Motivated by \jwst\ observations of AzTECC71, a far-infrared bright F150W-dropout with $z_{\rm phot}=5.7^{+0.8}_{-0.7}$, we complete a systematic search of F150W-dropouts with SCUBA-2 and ALMA detections to find the highest redshift dusty galaxies. Within our subsample, 16 are most similar to AzTECC71 due to faint F444W magnitudes ($>24$\,mag) and lack of counterparts in COSMOS2020. Despite high star formation rates ($\langle$SFR$\rangle=550^{+500}_{-360}$\,\mdot\,yr$^{-1}$) and large stellar masses ($\langle$log$_{10}$(\mstar)$\rangle=11.2^{+0.5}_{-0.4}$\,\mdot), these galaxies may not be particularly extreme for their presumed epochs according to offsets from the main sequence. We find that heavily obscured galaxies, which have inadvertently been omitted by past galaxy evolution studies, comprise roughly 20\% of their host population by mass. This population may, however, contribute significantly to the high mass end (log$_{10}$(\mstar/\mdot)$>11$) of the $z>4$ stellar mass function as up to 60\% could have been missed from previous studies.