Precipitation plausible: magnetized thermal instability in the intracluster medium
Precipitation plausible: magnetized thermal instability in the intracluster medium
Benjamin D. Wibking, G. Mark Voit, Brian W. O'Shea
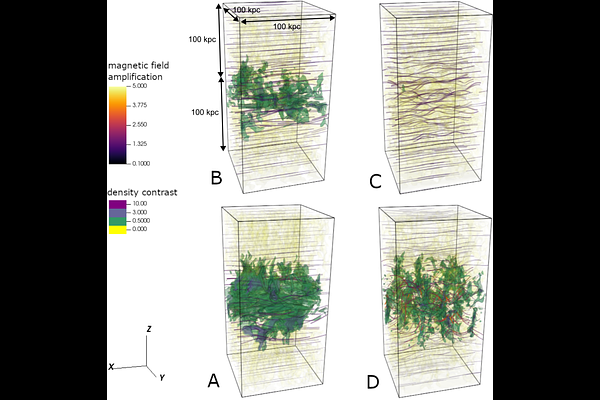
AbstractObservations of galaxy-cluster cores reveal that AGN feedback is strongly associated with both a short central cooling time ($t_{\rm c} \lesssim 10^9 \, {\rm yr}$) and accumulations of cold gas ($\lesssim 10^4 \, {\rm K}$). Also, the central ratio of cooling time to freefall time is rarely observed to drop below $t_{\rm c}/t_{\rm ff} \approx 10$, and large accumulations of cold gas are rarely observed in environments with $t_{\rm c} / t_{\rm ff} \gtrsim 30$. Here we show that the critical range -- $10 \lesssim t_{\rm c}/t_{\rm ff} \lesssim 30$ -- plausibly results from magnetized thermal instability. We present numerical simulations of magnetized stratified atmospheres with an initially uniform magnetic field. Thermal instability in an otherwise static atmosphere with $t_{\rm c}/t_{\rm ff} \approx 10$ progresses to nonlinear amplitudes, causing cooler gas to accumulate, as long as the background ratio of thermal pressure to magnetic pressure is $\beta \lesssim 100$. And in atmospheres with $t_{\rm c}/t_{\rm ff} \approx 20$, cooler gas accumulates for $\beta \lesssim 10$. Magnetized atmospheres are therefore much more likely to precipitate than unmagnetized atmospheres with otherwise identical properties. We hypothesize that AGN feedback triggered by accumulations of cold gas prevents $t_{\rm c}/t_{\rm ff}$ from dropping much below 10, because cold gas inevitably precipitates out of magnetized galactic atmospheres with lower ratios, causing $t_{\rm c}/t_{\rm ff}$ to rise.