Recovery of the Solar Cycle from Maunder-like Grand Minima Episodes: A Quantification of the Necessary Polar Flux Threshold
Recovery of the Solar Cycle from Maunder-like Grand Minima Episodes: A Quantification of the Necessary Polar Flux Threshold
Chitradeep Saha, Sanghita Chandra, Dibyendu Nandy
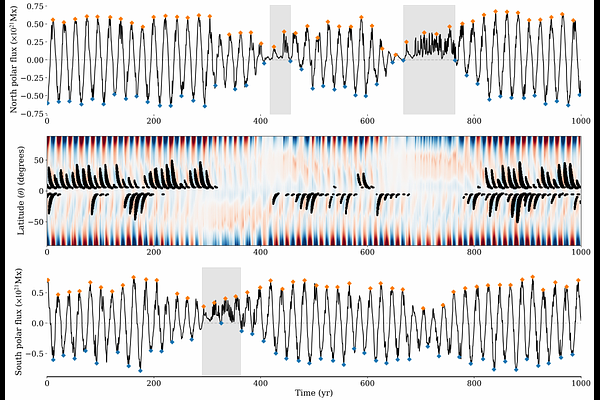
AbstractThe 11-yr cycle of sunspots undergo amplitude modulation over longer timescales. As a part of this long-term modulation in solar activity, the decennial rhythm occasionally breaks, with quiescent phases with very few sunspots observed over multiple decades. These episodes are termed as solar grand minima. Observation of solar magnetic activity proxies complemented by solar dynamo simulations suggests that the large-scale solar polar fields become very weak during this minima phases with a temporary halt in the polar field reversal. Eventually, with the accumulation of sufficient polar fluxes, the polarity reversal and regular cyclic activity is thought to resume, Using multi-millennial dynamo simulations with stochastic forcing, we quantify the polar flux threshold necessary to recover global solar polarity reversal and surmount grand minima phases. We find that the duration of a grand minimum is independent of the onset rate and does not affect the recovery rate. Our results suggest a method to forecast the Sun's recovery from a grand minima phase. However, based on our approach, we could not identify specific precursors that signal entry in to a grand minima phase -- implying that predicting the onset of grand minima remains an outstanding challenge.