Sulphur abundances in star-forming regions from optical emission lines: A new approach based on photoionization models consistent with the direct method
Sulphur abundances in star-forming regions from optical emission lines: A new approach based on photoionization models consistent with the direct method
Enrique Pérez-Montero, Borja Pérez-Díaz, José M. Vílchez, Igor A. Zinchenko, Asier Castrillo, Marta Gavilán, Sandra Zamora, Ángeles I. Díaz
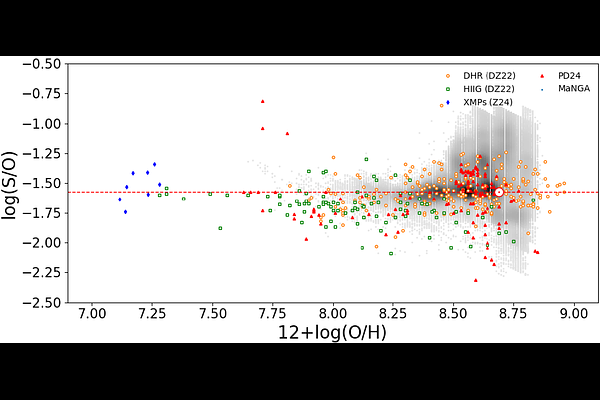
AbstractThe derivation of sulphur chemical abundances in the gas-phase of star-forming galaxies is explored in this work, using the emission lines produced in these regions in the optical part of the spectrum and by means of photoionization models. We adapted the code HII-CHI-mistry to account for these abundances by implementing additional grids of models that assume a variable sulphur-to-oxygen abundance ratio, beyond the commonly assumed solar ratio. The addition of these models, and their use in a new iteration of the code allows us to use sulphur lines to precisely estimate the sulphur abundance, even in the absence of auroral lines. This approach aligns with the results from the direct method, and no additional assumptions about the ionization correction factor are needed, as the models directly predict the total sulphur abundance. We applied this new methodology to a large sample of star-forming regions from the MaNGA survey, and we explored the variation of the S/O ratio as a function of metallicity, making corrections for the significant contribution from diffuse ionized gas, which particularly affects the [SII] emission. Our results indicate no significant deviations from the solar S/O value in the range 8.0 < 12+log(O/H) < 8.7, where the bulk of the MaNGA sample stays, , but also with possible enhancements of sulphur production both at low and high metallicity regimes. The latter may be linked to the depletion of oxygen in the gas-phase due to its incorporation onto dust grains