Distances of Supernova Remnants Associated with Neutron Stars in the Galaxy
Distances of Supernova Remnants Associated with Neutron Stars in the Galaxy
Xiaohan Chen, Shu Wang, Xiaodian Chen
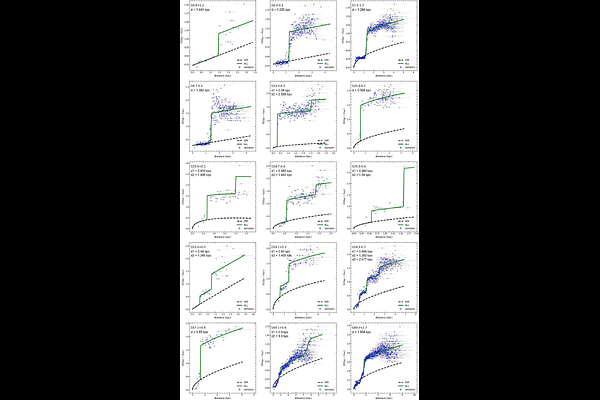
AbstractAccurate distance measurements to supernova remnants (SNRs) are essential for determining their physical parameters, such as size, age, explosion energy, and for constraining the properties of associated neutron stars (NSs). We present an extinction--distance method that combines precise Gaia DR3 photometry, parallax, and stellar parameters from the SHBoost catalog to homogeneously construct extinction--distance profiles for 44 NS-associated Galactic SNRs. Applying a statistical model, we identify clear extinction jumps along each sightline, corresponding to probable SNR distances. We classify the results into three reliability levels (A, B, and C), primarily based on comparisons with previously reported kinematic distances, supplemented by independent estimates from other methods. Our results show that the majority of reliable distances (17 Level A and 8 Level B) are located within 5 kpc, predominantly in the Local Arm. This study presents an independent and effective method for determining distances to SNRs, particularly for those with small angular sizes or located in the second and third Galactic quadrants. Although the current method is limited to within 5 kpc due to the precision constraints of Gaia parallax and photometry, the upcoming Gaia DR4 release, combined with complementary infrared data, will extend its applicability to more distant and heavily obscured SNRs, and help resolve kinematic distance ambiguities.