Scatter in the star formation rate-halo mass relation: secondary bias and its impact on line-intensity mapping
Scatter in the star formation rate-halo mass relation: secondary bias and its impact on line-intensity mapping
Rui Lan Jun, Tom Theuns, Kana Moriwaki, Sownak Bose
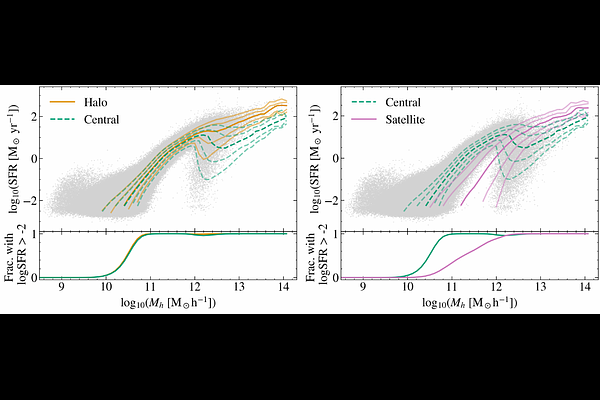
AbstractWe use the IllustrisTNG cosmological hydrodynamical simulations to study the impact of secondary bias -- specifically, the correlation between star formation rate (SFR) and halo bias at fixed halo mass -- on the line-intensity mapping (LIM) power spectrum. In LIM, the galaxy contributions are flux-weighted, and for many emission lines (e.g., H$\alpha$), flux scales with SFR. We show that the (ensemble-averaged) large-scale two-halo term of the power spectrum depends only on the mean luminosity-halo mass relation if the scatter is uncorrelated with halo bias. However, when luminosity correlates with halo bias at fixed mass, this assumption breaks down. In IllustrisTNG, this secondary bias increases the two-halo term by 5 per cent at $z \sim 1.5$ compared to a model with random scatter. We also find that SFRs of central and satellite galaxies are correlated, enhancing the one-halo term -- sensitive to intra-halo SFR distribution -- by 10 per cent relative to random pairings. To mitigate secondary bias in the two-halo term, we identify halo concentration (for haloes with mass $\log M_h \lesssim 12$) and satellite mass (for $\log M_h \gtrsim 12$) as effective secondary parameters. These results highlight the need to account for secondary bias when building mock catalogues and interpreting LIM observations.