James Webb Space Telescope Observations of the Nearby and Precisely-Localized FRB 20250316A: A Potential Near-IR Counterpart and Implications for the Progenitors of Fast Radio Bursts
James Webb Space Telescope Observations of the Nearby and Precisely-Localized FRB 20250316A: A Potential Near-IR Counterpart and Implications for the Progenitors of Fast Radio Bursts
Peter K. Blanchard, Edo Berger, Shion E. Andrew, Aswin Suresh, Kohki Uno, Charles D. Kilpatrick, Brian D. Metzger, Harsh Kumar, Navin Sridhar, Amanda M. Cook, Yuxin Dong, Tarraneh Eftekhari, Wen-fai Fong, Walter W. Golay, Daichi Hiramatsu, Ronniy C. Joseph, Victoria M. Kaspi, Mattias Lazda, Calvin Leung, Kiyoshi W. Masui, Juan Mena-Parra, Kenzie Nimmo, Aaron B. Pearlman, Vishwangi Shah, Kaitlyn Shin, Sunil Simha
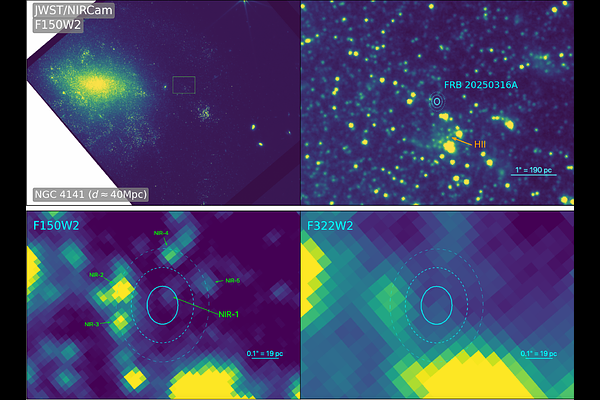
AbstractWe present deep James Webb Space Telescope near-infrared imaging to search for a quiescent or transient counterpart to FRB 20250316A, which was precisely localized with the CHIME/FRB Outriggers array to an area of $11\times13$ pc in the outer regions of NGC 4141 at $d\approx40$ Mpc. Our F150W2 image reveals a faint source near the center of the FRB localization region ("NIR-1"; $M_{\rm F150W2}\approx-2.5$ mag; probability of chance coincidence $\approx0.36$), the only source within $\approx2.7\sigma$. We find that it is too faint to be a globular cluster, young star cluster, red supergiant star, or a giant star near the tip of the red giant branch (RGB). It is instead consistent with a red giant near the RGB "clump" or a massive ($\gtrsim20$ M$_{\odot}$) main sequence star, although the latter explanation is less likely. The source is too bright to be a supernova remnant, Crab-like pulsar wind nebula, or isolated magnetar. Alternatively, NIR-1 may represent transient emission, namely a dust echo from an energetic outburst associated with the FRB, in which case we would expect it to fade in future observations. We explore the stellar population near the FRB and find that it is composed of a mix of young massive stars ($\sim10-100$ Myr) in a nearby HII region that extends to the location of FRB 20250316A, and old evolved stars ($\gtrsim$ Gyr). The overlap with a young stellar population, containing stars of up to $\approx20$ M$_\odot$, may implicate a neutron star / magnetar produced in the core collapse of a massive star as the source of FRB 20250316A.