SETI@home: Data Analysis and Findings
SETI@home: Data Analysis and Findings
David P. Anderson, Eric J. Korpela, Dan Werthimer, Jeff Cobb, Bruce Allen
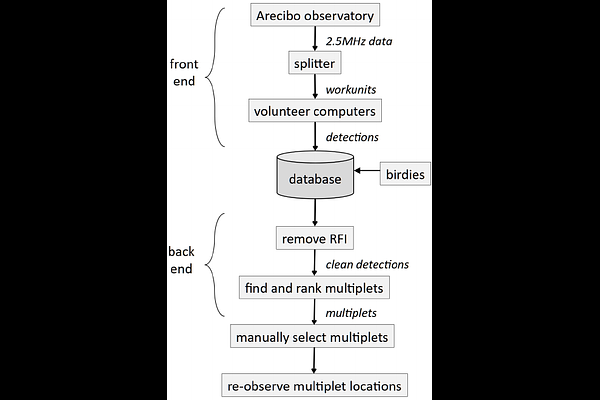
AbstractSETI@home is a radio Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) project that looks for technosignatures in data recorded at the Arecibo Observatory. The data were collected over a period of 14 years and cover almost the entire sky visible to the telescope. The first stage of data analysis found billions of detections: brief excesses of continuous or pulsed narrowband power. The second stage removed detections that were likely radio frequency interference (RFI), then identified and ranked signal candidates: groups of detections, possibly spread over the 14 years, that plausibly originate from a single cosmic source. We manually examined the top-ranking signal candidates and selected a few hundred. In the third and final stage we are reobserving the corresponding sky locations and frequency ranges using the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) radio telescope. This paper covers SETI@home's second stage of data analysis. We describe the algorithms used to remove RFI and to identify and rank signal candidates. To guide the development of these algorithms, we used artificial candidate birdies that model persistent ET signals with a range of power, bandwidth, and planetary motion parameters. This approach also allowed us to estimate the sensitivity of our detection system to these signals.