Discovery of Volatile Gas in the Giant Impact Disk around the 150-Myr old HD 23514
Discovery of Volatile Gas in the Giant Impact Disk around the 150-Myr old HD 23514
Kate Y. L. Su, Attila Moór, Chengyan Xie, Ilaria Pascucci, George H. Rieke, Ágnes Kóspál, Mark C. Wyatt, Péter Ábrahám, Luca Matrà, Zoe Roumeliotis, D. J. Wilner
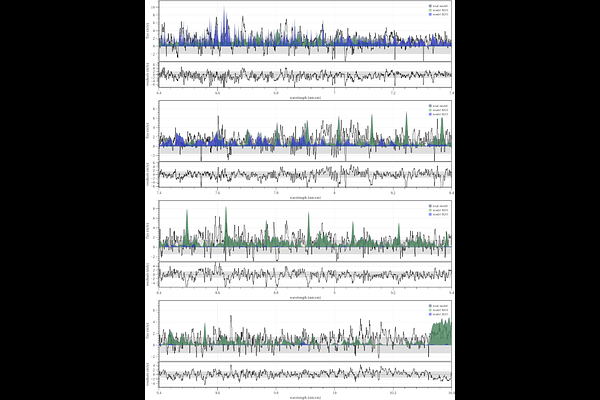
AbstractWe report the discovery of CO$_2$ gas emission around HD 23514, an F5V star in the $\sim$150 Myr-old Pleiades cluster, hosting one of the rare giant-impact disks with unique mineralogy dominated by silica dust. We show that the dust feature remains stable over several decades, and that the sub-$\mu$m grains, which give rise to the $\sim$9 $\mu$m feature, are co-spatial with the hot CO$_2$ molecules within the sub-au vicinity of the star. Examining the Spitzer spectrum taken 15 years earlier, we show that the CO$_2$ emission was also present at 4.3 $\sigma$ significance. The existence of tiny silica grains and volatile gas requires special conditions to prevent the rapid loss caused by stellar radiation pressure and photodissociation. We explore several pathways explaining the observed properties and suggest that a past giant impact and/or stripping atmospheric event, involving large bodies with volatile content similar to the carbonaceous chondritic material, can simultaneously explain both the silica and volatile emission. Our discovery provides an important context for the amount of volatiles that a newly formed planet or the largest planetesimals could retain during the giant impact phase in the early solar system evolution.