Saturns, but not super-Jupiters, occur more frequently in the presence of inner super-Earths
Saturns, but not super-Jupiters, occur more frequently in the presence of inner super-Earths
Etienne Lefevre-Forjan, Gijs D. Mulders
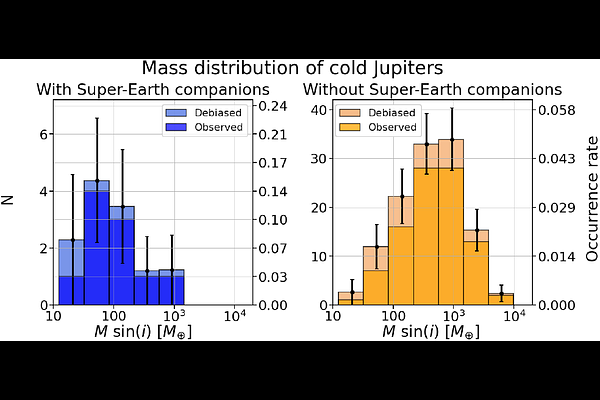
AbstractStudies from recent years have reached different conclusions regarding how frequently super-Earths are accompanied by long period giant planets and vice versa. This relation has been predicted to be mass dependent by planet formation models. We investigate that as the origin of the discrepancy using a radial velocity sample: the California Legacy Survey. We perform detection completeness corrections in order to discard detection bias as a possible explanation to our results. After bias corrections, we find that cold Jupiters are 5.65 times more massive when not in company of an inner super-Earth, while super-Earths are not significantly more massive while in company of an outer giant planet. We also report an occurrence enhancement for Saturns (median projected mass of 0.6MJ) while in presence of a super-Earth by a factor of 4, and for super-Earths in presence of Saturns by the same factor. This positive correlation disappears for super-Jupiters (median projected mass of 3.1MJ). These results show that while cold Jupiters are generally accompanied by inner super-Earths, this does not hold for the largest giant planets, such as those that will be discovered by Gaia, which will likely not be accompanied by transiting planets. The mass dependence, in combination with different detection limits of different surveys, may explain the discrepancies concerning occurrence relations between cold Jupiters and super-Earths.