Lense-Thirring Precession Modulates Repeated Lensing of Continues Gravitational Wave Source from AGN Disks
Lense-Thirring Precession Modulates Repeated Lensing of Continues Gravitational Wave Source from AGN Disks
Yu-Zhe Li, Wen-Long Xu, Yi-Gu Chen, Wei-Hua Lei
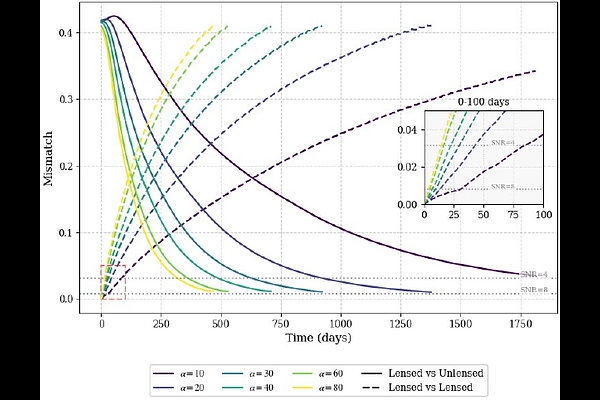
AbstractGravitational lensing of gravitational waves (GWs) offers a novel observational channel that complements traditional electromagnetic approaches and provides unique insights into the astrophysical environments of GW sources. In this work, we investigate the repeated lensing of continuous gravitational wave (CW) sources in active galactic nucleus (AGN) disks by central supermassive black holes (SMBHs), focusing on the imprint of SMBH spin via the Lense-Thirring (LT) effect. Although typically weak and challenging to observe, the spin-induced precession of source orbits can accumulate over time, thereby modulating the lensing geometry. Such modulations influence the magnification, duration, and waveform structure of each repeated lensing event, and enhance the overall probability of lensing occurrences. Using matched filtering, we demonstrate that spin-dependent signatures may be detectable, suggesting that lensed CW signals could serve as an indirect probe of SMBH spin in AGNs.