Lyman-Break Galaxies in the Mpc-Scale Environments Around Three $z\sim7.5$ Quasars With JWST Imaging
Lyman-Break Galaxies in the Mpc-Scale Environments Around Three $z\sim7.5$ Quasars With JWST Imaging
Maria Pudoka, Feige Wang, Xiaohui Fan, Jinyi Yang, Jaclyn Champagne, Zijian Zhang, Sofía Rojas-Ruiz, Eduardo Bañados, Silvia Belladitta, Sarah E. I. Bosman, Anna-Christina Eilers, Xiangyu Jin, Hyunsung D. Jun, Mingyu Li, Weizhe Liu, Chiara Mazzucchelli, Jan-Torge Schindler, Julien Wolf, Yunjing Wu
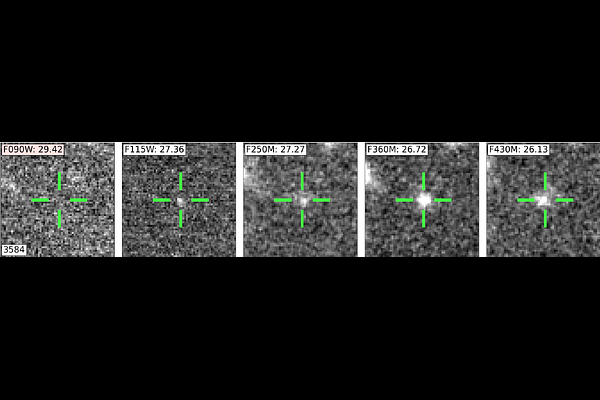
AbstractWe study the Mpc-scale environments of the three highest redshift luminous quasars at $z\geq 7.5$ (J031343.84-180636.40, J134208.11+092838.61, and J100758.27+211529.21) to understand their connection to large-scale structure. Cosmological simulations show that these early supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are expected to form in the most massive dark matter halos. Therefore, it is expected that they are anchors of galaxy overdensities if luminous matter traces the underlying dark matter structure of the Universe. Using JWST NIRCam (F090W/F115W/F250M/F360M/F430M) imaging, we observe the large-scale structure out to $\sim13$ comoving Mpc around these quasars. We select F090W-dropout Lyman Break galaxies (LBGs) and F430M-excess [OIII] emitters in the three fields. We find 18, 21, and 6 LBG candidates in the fields of J0313, J1342, and J1007, respectively, resulting in a wide range of overdensities ($1+\delta \sim 19,\,24,$ and $7$). The photometric redshifts indicate serendipitous foreground and background overdensities in the J0313 field. The joint angular autocorrelation of the combined LBG sample shows significant clustering on $<1.8$ comoving Mpc scales, demonstrating that the selected galaxies are likely associated with the large-scale structure surrounding the quasars. This first systematic study of $z\sim 7.5$ quasars shows a diverse set of quasar environments at the onset of their formation, providing empirical data to help constrain theoretical predictions of early structure formation.