Constraining the lensing dispersion from the angular clustering of binary black hole mergers
Constraining the lensing dispersion from the angular clustering of binary black hole mergers
Fumihiro Chuman, Masamune Oguri
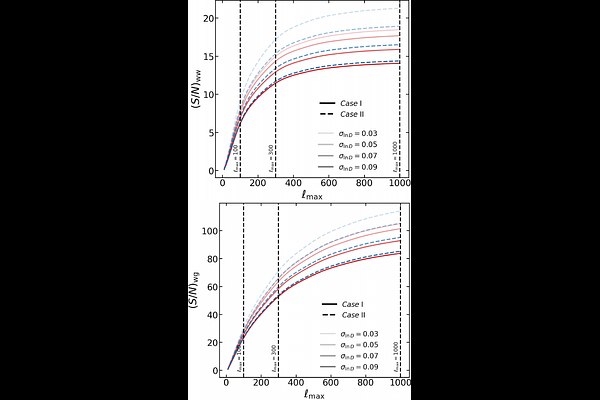
AbstractGravitational waves from inspiraling compact binaries provide direct measurements of luminosity distances and serve as a powerful probe of the high-redshift Universe. In addition to their role as standard sirens, they offer an opportunity to constrain small-scale density fluctuations through the dispersion in the distance-redshift relation induced by gravitational lensing. We propose a method to constrain this lensing dispersion without requiring the redshift information by analyzing the angular clustering of gravitational wave sources. Our formalism incorporating second-order lensing effects in the luminosity distance shows that the amplitude of the auto-correlation angular clustering decreases with increasing lensing dispersion. While we show that the auto-correlation signal is detected with sufficient signal-to-noise ratios in future gravitational wave experiments, there exists a strong degeneracy between the lensing dispersion and the linear bias of gravitational wave sources. We demonstrate that this degeneracy is partially broken by a joint analysis of the auto-correlation of gravitational wave sources and the cross-correlation with galaxies whose redshifts are known. This approach enhances the use of gravitational waves as a cosmological probe at high redshifts.