A Joint JWST and HST View of Omega Centauri: Multiple Stellar Populations and Their Kinematics
A Joint JWST and HST View of Omega Centauri: Multiple Stellar Populations and Their Kinematics
T. Ziliotto, A. P. Milone, G. Cordoni, A. F. Marino, M. V. Legnardi, E. Dondoglio, E. Bortolan, F. Muratore
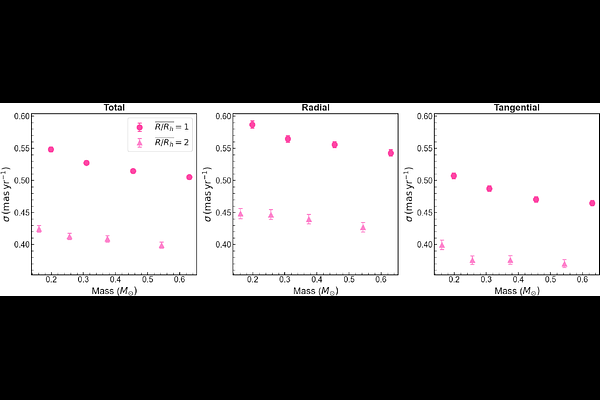
AbstractWe combine F115W and F277W images collected with the Near Infrared Camera of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) with multi-band, multi-epoch Hubble Space Telescope (HST) observations of Omega Centauri to investigate its multiple stellar populations and internal kinematics. Our study focuses on a region spanning $\sim$0.9 to $\sim$2.3 half-light radii from the cluster center, largely unexplored by HST and JWST. Using chromosome maps, we identify the principal populations along the upper main sequence and among M-dwarfs, distinguishing lower-stream (LS) stars, chemically akin to first-generation globular cluster stars with similar metallicities, and upper-stream (US) stars, enriched in helium and nitrogen but oxygen-poor. Both streams also host subpopulations with varying metallicities. We find radially anisotropic motions, with US stars exhibiting significantly stronger anisotropy than LS stars. Subdividing the US into extreme and intermediate light-element populations reveals a gradient in anisotropy, with intermediate stars lying between the LS and extreme US populations. However, metal-rich and metal-poor stars within each stream show moderate kinematic differences. The LS stars show higher angular momentum and dispersion compared to US stars, and also exhibit stronger systemic rotation and tangential proper-motion skewness, further highlighting their kinematic divergence. Finally, leveraging a mass range of $\sim$0.15 - 0.7 solar masses, we detect a low degree of energy equipartition for all cluster stars, which decreases with radial distance from the cluster center.