A third star in the HAT-P-7 system, and a new dynamical pathway to misaligned hot Jupiters
A third star in the HAT-P-7 system, and a new dynamical pathway to misaligned hot Jupiters
Eritas Yang, Yubo Su, Joshua N. Winn
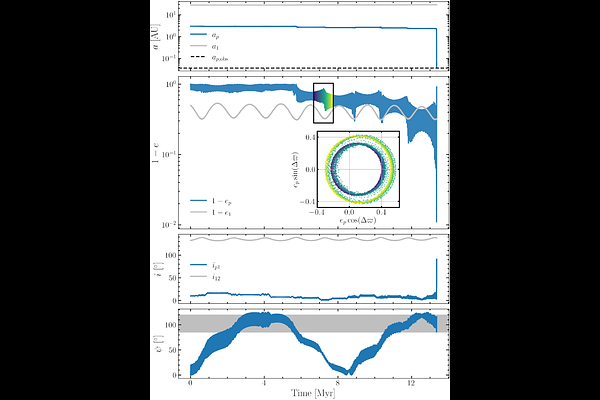
AbstractThe retrograde orbit of the hot Jupiter HAT-P-7b is suggestive of high-eccentricity migration caused by dynamical interactions with a massive companion. However, the only other known body in the system is an M dwarf located $\sim$10$^3$~AU away, too distant to cause high-eccentricity migration without fine tuning. Here we present transit-timing and radial-velocity evidence for an additional stellar companion with semi-major axis $32^{+16}_{-11}$~AU, eccentricity $0.76^{+0.12}_{-0.26}$, and minimum mass $0.19^{+0.11}_{-0.06}$~$\rm M_\odot$. We investigate several dynamical routes by which this nearby companion star could have played a role in converting a cold Jupiter into the retrograde hot Jupiter that is observed today. Of particular interest is a novel "eccentricity cascade" mechanism involving both of the companion stars: the outer companion periodically excites the eccentricity of the inner companion through von Zeipel-Lidov-Kozai (ZLK) cycles, and this eccentricity excitation is slowly transferred to the cold Jupiter via successive close encounters, eventually triggering its high-eccentricity migration. The plausibility of this mechanism in explaining HAT-P-7b shows that stellar companions traditionally considered too distant to cause hot Jupiter formation might nevertheless be responsible, with the aid of closer-orbiting massive companions. With these developments, HAT-P-7b is one of the few hot Jupiters for which a complete high-eccentricity migration history can be simulated based only on observed bodies, rather than invoking bodies that are beneath detection limits or that are no longer in the system.