PICT -- A Differentiable, GPU-Accelerated Multi-Block PISO Solver for Simulation-Coupled Learning Tasks in Fluid Dynamics
PICT -- A Differentiable, GPU-Accelerated Multi-Block PISO Solver for Simulation-Coupled Learning Tasks in Fluid Dynamics
Aleksandra Franz, Hao Wei, Luca Guastoni, Nils Thuerey
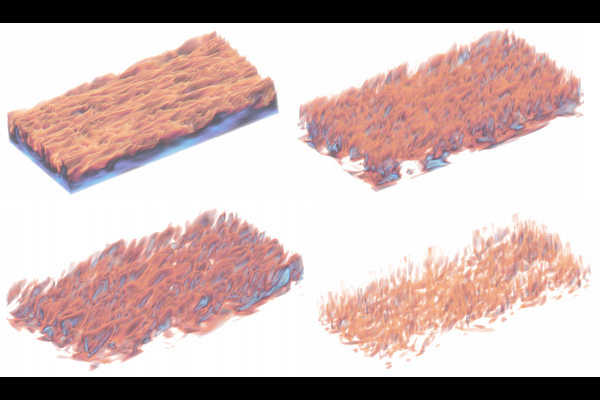
AbstractDespite decades of advancements, the simulation of fluids remains one of the most challenging areas of in scientific computing. Supported by the necessity of gradient information in deep learning, differentiable simulators have emerged as an effective tool for optimization and learning in physics simulations. In this work, we present our fluid simulator PICT, a differentiable pressure-implicit solver coded in PyTorch with Graphics-processing-unit (GPU) support. We first verify the accuracy of both the forward simulation and our derived gradients in various established benchmarks like lid-driven cavities and turbulent channel flows before we show that the gradients provided by our solver can be used to learn complicated turbulence models in 2D and 3D. We apply both supervised and unsupervised training regimes using physical priors to match flow statistics. In particular, we learn a stable sub-grid scale (SGS) model for a 3D turbulent channel flow purely based on reference statistics. The low-resolution corrector trained with our solver runs substantially faster than the highly resolved references, while keeping or even surpassing their accuracy. Finally, we give additional insights into the physical interpretation of different solver gradients, and motivate a physically informed regularization technique. To ensure that the full potential of PICT can be leveraged, it is published as open source: https://github.com/tum-pbs/PICT.