Truly Self-Improving Agents Require Intrinsic Metacognitive Learning
Truly Self-Improving Agents Require Intrinsic Metacognitive Learning
Tennison Liu, Mihaela van der Schaar
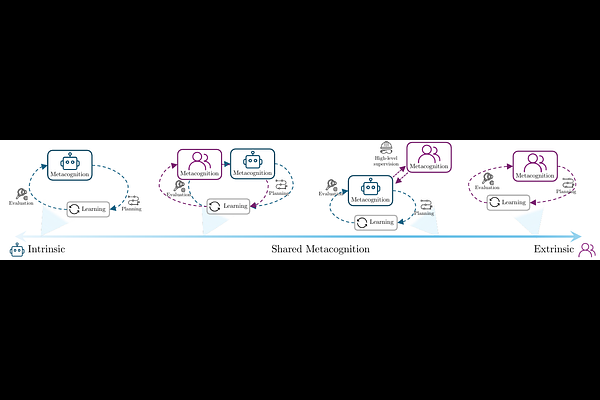
AbstractSelf-improving agents aim to continuously acquire new capabilities with minimal supervision. However, current approaches face two key limitations: their self-improvement processes are often rigid, fail to generalize across tasks domains, and struggle to scale with increasing agent capabilities. We argue that effective self-improvement requires intrinsic metacognitive learning, defined as an agent's intrinsic ability to actively evaluate, reflect on, and adapt its own learning processes. Drawing inspiration from human metacognition, we introduce a formal framework comprising three components: metacognitive knowledge (self-assessment of capabilities, tasks, and learning strategies), metacognitive planning (deciding what and how to learn), and metacognitive evaluation (reflecting on learning experiences to improve future learning). Analyzing existing self-improving agents, we find they rely predominantly on extrinsic metacognitive mechanisms, which are fixed, human-designed loops that limit scalability and adaptability. Examining each component, we contend that many ingredients for intrinsic metacognition are already present. Finally, we explore how to optimally distribute metacognitive responsibilities between humans and agents, and robustly evaluate and improve intrinsic metacognitive learning, key challenges that must be addressed to enable truly sustained, generalized, and aligned self-improvement.