Chemical Signatures of Population III Stars in Damped Lyman-$α$ Absorption Systems at $z \approx 6$
Chemical Signatures of Population III Stars in Damped Lyman-$α$ Absorption Systems at $z \approx 6$
Eli Visbal, Greg L. Bryan, Zoltan Haiman
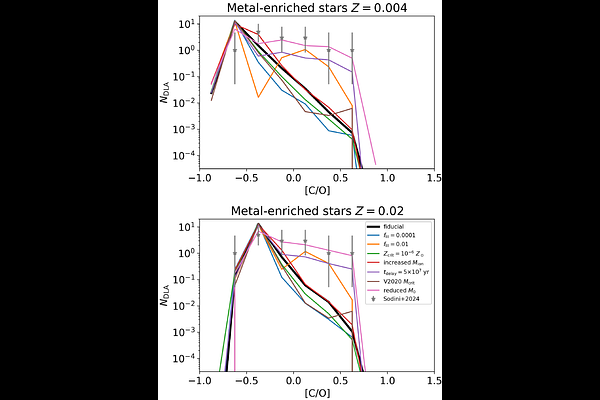
AbstractRecently, Sodini et al. (2024) presented a sample of OI damped Lyman-$\alpha$ absorption system (DLA) analogs at $z\sim6$ that contain possible chemical signatures of Population III (Pop III) stars. In this paper, we use an N-body simulation-based semi-analytic model of the first stars and galaxies to predict the impact of Pop III stars on high-redshift DLAs. These Pop III DLA predictions are the first to include a number of important physical effects such as Lyman-Werner (LW) feedback, reionization, and external metal enrichment (all of which account for three-dimensional spatial fluctuations caused by halo clustering). We predict the abundance of DLAs as a function of their carbon-to-oxygen ratios ([C/O]). We find that our fiducial model is strongly ruled out by the data as it contains too few high-[C/O] DLAs, which have metals primarily from Pop III stars. However, increasing the delay time between Pop III and metal-enriched star formation due to supernovae feedback leads to better agreement with the data. Our results suggest that DLA analogs at $z\sim6$ are a promising probe of Pop III star formation for two key reasons. First, for reasonable parameter choices there are significant numbers of DLAs with metals primarily originating from Pop III stars. Second, we find that the number of DLAs with substantial Pop III contributions depends strongly on the Pop III star formation efficiency and the delay time between Pop III and metal-enriched star formation.