Multiplexed Data-Independent Acquisition (mDIA) to Profile Extracellular Vesicle Proteomes
Multiplexed Data-Independent Acquisition (mDIA) to Profile Extracellular Vesicle Proteomes
Liu, Y.-K.; Miller, N.; Hadisurya, M.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, W. A.
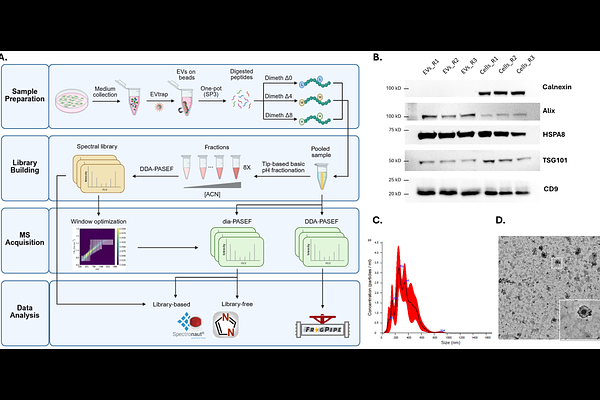
AbstractExtracellular vesicles (EVs) have gained increasing attention with their intriguing biological functions and their molecular cargoes serving as potential biomarkers for various diseases, including cancers. A relatively lower abundance of EV proteins compared to cellular counterparts necessitates sensitive and accurate quantitative proteomic strategies. Multiplexed proteomics combined with data-independent acquisition (mDIA) has shown promise for improving sensitivity and quantification over traditional DDA and label-free methods. Despite this, mDIA pipelines that utilize various types of spectral libraries and search software suites have not been thoroughly evaluated with EV proteome samples. In this study, we aim to establish a robust mDIA pipeline based on dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics of EVs. EVs were isolated using the extracellular vesicle total recovery and purification (EVtrap) technique and processed directly through an on-bead one-pot sample preparation workflow to obtain digested peptides. We evaluated different mDIA pipelines, including library-free and library-based DIA on the timsTOF HT platform. Results showed that library-based DIA, with project-specific spectral libraries generated from StageTip-based fractionation, outperformed other pipelines in protein identification and quantification. We demonstrated for the first time EV proteome landscape changes caused by the IDH1 mutation and inhibitor treatment in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, highlighting the utility of mDIA in EV-based biomarker discovery.