NETSseq Reveals Inflammatory and Aging Mechanisms in Distinct Cell Types Driving Cerebellar Decline in Ataxia Telangiectasia
NETSseq Reveals Inflammatory and Aging Mechanisms in Distinct Cell Types Driving Cerebellar Decline in Ataxia Telangiectasia
Stirparo, G. G.; Xu, X.; Thompson, T.; Page, K.; Harvey, J. R.; Cadwalladr, D.; Lawrence, J.; Burley, R. J.; Juvvanapudi, J.; Roberts, M.; Barker, D. F.; Mulligan, V.; Sherlock, C.; Lizio, M.; Christie, L.; Mudaliar, M.; Sheardown, S.; Margus, B.; Thompson, C.; Dickson, L.; Brice, N. L.; Carlton, M. B.; Powell, J. A.; Dawson, L. A.
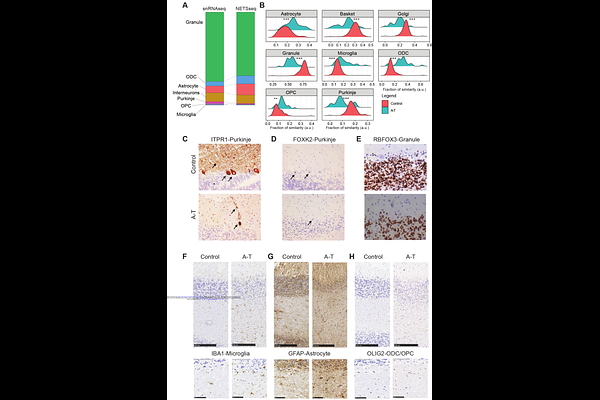
AbstractAtaxia-telangiectasia (A-T) is a rare, autosomal recessive, multisystem disorder caused by mutations in the Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM) gene and is characterized by a devastating and progressive neurological pathology. The cellular and molecular changes driving the neurological abnormalities associated with A-T are not well understood. Here, we applied our proprietary Nuclear Enriched Transcript Sort sequencing (NETSseq) platform to investigate changes in cell type composition and gene expression in human cerebellar post-mortem tissue from A-T and control donors. We found dysregulation in neurotransmitter signaling in granule neurons, potentially underlying the impaired motor coordination in A-T. Astrocytes and microglia have evidence of accelerated aging, with astrocytes being characterized by neurotoxic signatures, while microglia showed activation of DNA damage response pathways. Compared to single-nuclei technologies, NETSseq provided a more robust detection of genes with low abundance, a higher cell type specific expression pattern, and significantly lower levels of cross-contamination. These findings highlight the importance of NETSseq as a resource for investigating mechanisms and biological processes associated with disease, providing high-sensitivity, cell-specific insights to advance targeted therapies for neurodegenerative diseases.