Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a potential therapeutic target for cisplatin induced peripheral neuropathy in breast cancer
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a potential therapeutic target for cisplatin induced peripheral neuropathy in breast cancer
El-Baroudy, H.; Delgadillo, X. M.; Bamania, N.; Sivakumar, B.; Dwivedi, S.; Chowdhury, B.; Joseph, N.; Pathak, S.; Mizkus, S.; Ahmed, S.; Krishnan, A.
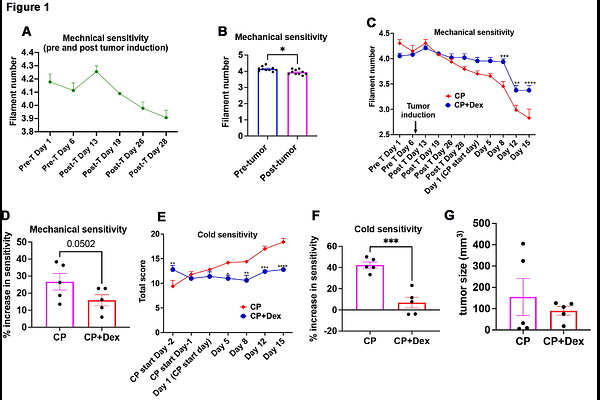
AbstractBackground: Cisplatin (CP) is an effective chemotherapy drug for several cancers. However, the use of CP is associated with peripheral neuropathy, a painful nerve disorder. Unfortunately, no therapies are available for CP-induced peripheral neuropathy (CisIPN). This study explored the role of a cytokine, the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), as a potential therapeutic target for CisIPN. Methods: The role of neuroinflammation and MIF in CisIPN was evaluated in mice models of CisIPN, with and without breast cancer, after treatment with the anti-inflammatory drug Dexamethasone (Dex). Circulating MIF levels in animals were examined using ELISA. Pharmacological inhibition of MIF was achieved using the small molecule inhibitors, CPSI-1306 and ISO-1. Mechanical and thermal sensitivities of animals were assessed using von frey filament and cold acetone assays. Macrophage infiltration in peripheral nerve tissues was examined using CD68 and Iba-1 staining. Results: Our results showed that Dex suppressed mechanical hyperalgesia in CisIPN animals, which was accompanied by downregulation of MIF. We also found that circulating MIF levels were increased in CisIPN animals. Furthermore, direct inhibition of MIF using CPSI-1306 and ISO-1 led to suppression of mechanical hyperalgesia, without compromising the anti-tumor efficacy of CP, in CisIPN animals. We did not find any significant change in macrophage infiltration in the peripheral nerve tissues of CisIPN animals. Immunostaining results indicated that sensory neurons in the DRGs and Schwann Cells in the sciatic nerves are potential sources for increased MIF in CisIPN. Interpretation: Overall, our results strongly suggest that MIF is a promising therapeutic target for CisIPN.