Lymphatic Malformations with Activating KRAS Mutations Impair Lymphatic Valve Development Through Matrix Metalloproteinases
Lymphatic Malformations with Activating KRAS Mutations Impair Lymphatic Valve Development Through Matrix Metalloproteinases
Mastrogiacomo, D. M.; Price, A.; Fu, Y.; Banerjee, R.; Knauer, L. A.; Li, K.; Yang, Y.; Davis, G. E.; Dellinger, M.; Scallan, J. P.
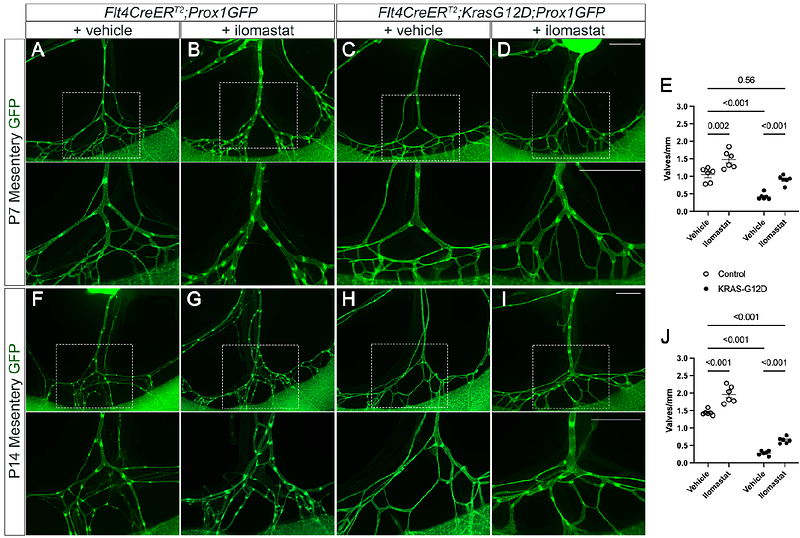
AbstractBACKGROUND: Lymphatic malformations (LMs) are lesions due to inherited or somatic mutations that lead to a defective lymphatic vasculature. Activating KRAS mutations have been identified recently in LM patients with lymphedema, chylous ascites, or life-threatening chylothorax. In a LM mouse model, KRAS mutations are associated with a loss of lymphatic valves, which has been proposed to cause chylothorax via retrograde lymph flow into the pleural space. However, the mechanisms underlying the loss of lymphatic valves are unknown. METHODS: To investigate the mechanisms leading to valve loss, we combined the lymphatic-specific and tamoxifen-inducible Flt4CreERT2 with Kras-loxP-stop-loxP-G12D (Kras+/G12D) mice and Prox1GFP reporter mice to induce the restricted expression of KRAS-G12D and enable valve quantification in postnatal pups. Human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells (hdLECs) expressing KRAS-G12D were probed for changes in mRNA and protein expression with qRT-PCR, western blot, and gel zymography, and mechanistic studies were performed using 3D cell culture in collagen matrices. RESULTS: Our data showed that lymphatic-specific expression of KRAS-G12D significantly attenuated valve development in the mesentery, diaphragm, and ear skin. qRT-PCR, western blot, and gel zymography using hdLECs expressing KRAS-G12D revealed the upregulation of the plasminogen activator (PA) pathway and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). The MMPs were sufficiently activated by plasmin, the product of the PA pathway, in hdLECs grown in a 3D collagen matrix, indicating a role for MMPs in the degradation of valve ECM core. Furthermore, a broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor given to Flt4CreERT2;Kras+/G12D mice rescued lymphatic valve development. CONCLUSIONS: We conclude that hyperactive KRAS signaling upregulates MMPs that become excessively activated by the upregulation of the PA pathway. MMPs then degrade the lymphatic valve ECM core preventing valve formation.