Assessing analysis methods of brain synchrony in social interaction: Simulation-based comparison
Assessing analysis methods of brain synchrony in social interaction: Simulation-based comparison
Morimoto, S.; Minagawa, Y.
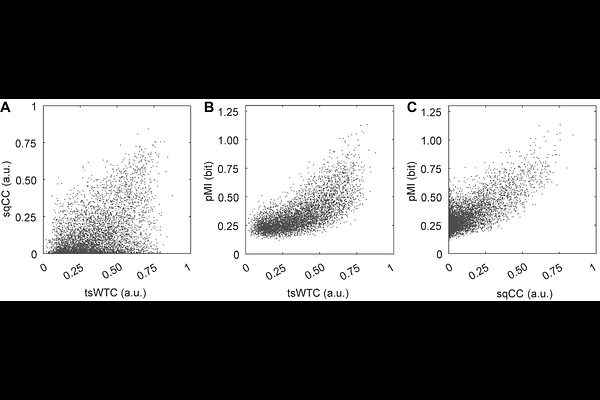
AbstractInter-brain synchrony is an essential measure for investigating social interactive behaviour via hyperscanning. While functional near-infrared spectroscopy is a unique modality for measuring this index in dynamic, real-world interactions, methods to adequately assess inter-brain relationships have not been firmly established, and the overall picture remains unclear. Consequently, in this article, we first briefly summarize analysis methods for examining social interaction by dividing them into static and dynamic measures. Among these, we focus on measures of synchrony and their assessment in correlating behaviours, conducting a simulation-based comparison and analysis. Specifically, we directly compared static and dynamic variants of wavelet transform coherence (WTC), Pearson\'s correlation coefficient (CC), and phase mutual information (pMI) using a real fNIRS dataset. Results showed a significant divergence between WTC and CC, while WTC and pMI exhibited similar patterns as static measures. Overall, WTC was suggested to better identify synchrony due to its non-linear, instantaneous, and robust nature. For the latter part, based on other simulation analyses, we propose a new method using generalized linear model (GLM) regression. Simulations with synthetic fNIRS data supported the effectiveness of our proposed method, which can capture the dynamic relationships between inter-brain synchrony and behaviour, even during free interaction.