Microbes regulate glomerular filtration rate in health and chronic kidney disease in mice
Microbes regulate glomerular filtration rate in health and chronic kidney disease in mice
Xu, J.; Verma, E.; Sanchez, J.; Gharaie, S.; Jeong, S.; Gooya, M.; Gupta, K.; Rabb, H.; Pluznick, J. L.
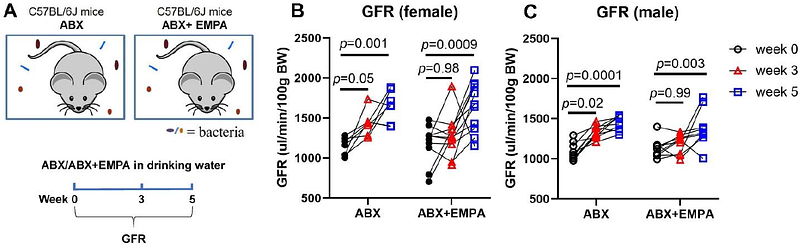
AbstractMicrobes are implicated in a variety of host physiological and pathophysiological processes. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that microbes modulate glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Microbiota were depleted in mice using oral antibiotics (ABX; a mixture of ampicillin, neomycin, and vancomycin). GFR was significantly increased in ABX-treated mice. To confirm that the increase in GFR was due to decreased microbes, we also measured GFR in germ-free (GF) mice. GFR was increased in GF mice as compared to both conventional and conventionalized GF (CGF) mice. We next used the murine adenine diet model to ask if suppressing gut microbes with ABX also increases GFR in a setting of chronic kidney disease (CKD), where GFR is impaired. In females on an adenine diet, ABX increased GFR versus adenine alone on weeks 4 and 6. In males, ABX elevated GFR on week 2. Adenine diet significantly increased plasma creatinine and kidney fibrosis; this was suppressed by ABX in both sexes. To explore the mechanism of this increase, we tested the hypothesis that altered tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF) contributes to elevated GFR using the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin (EMPA); EMPA impairs Na+ reabsorption in the proximal tubule, altering TGF. We found that EMPA impaired ABX-induced GFR increases on week 3 but not week 5, suggesting that altered TGF contributes to the initial increase in GFR. In conclusion, the microbiome plays a key role in setting baseline GFR by a mechanism that partially involves TGF, and, suppressing gut microbes can elevate GFR even in CKD.