Development of an open-pollinated genetic mapping framework to facilitate the identification of QTL in apples
Development of an open-pollinated genetic mapping framework to facilitate the identification of QTL in apples
Hickok, D.; Khan, A.; Robbins, K.
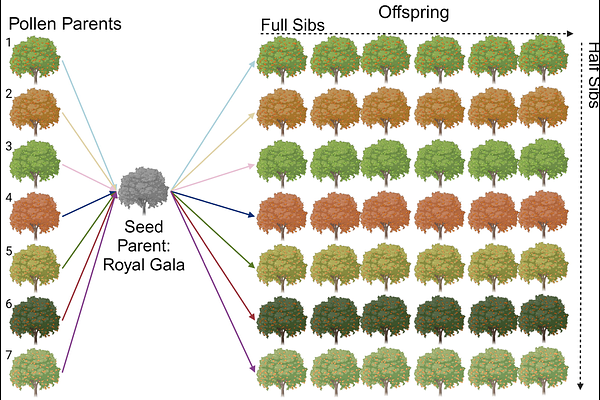
AbstractGenetic mapping of traits in apples (Malus domestica), a temperate woody perennial, is challenging due to high heterozygosity, long juvenility, and extensive spatial maintenance requirements for the populations. These factors limit the effective use of traditional Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) mapping methods in identifying the genetic basis of traits critical for apple production, marketability and sustainability. We explored the use of open-pollinated (OP) genetic mapping as an alternative to conventional bi-parental QTL mapping and genome wide association studies (GWAS). A QTL was simulated and the performance of a mixed linear model (MLM) and a multi-locus mixed model (MLMM) in QTL mapping accuracy was compared using a genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) dataset of seven interspecific Royal Gala x M. sieversii bi-parental F1 populations. The simulation results show that the MLMM outperformed the MLM by accurately identifying the simulated QTL. Analysis of power indicated that a population size of 137 individuals is required to reach an = 0.8 for a simulated major effect QTL. Mapping resolution analysis showed that a population size of 470-600 individuals, depending on local recombination rates, is necessary to achieve high resolution within the OP population. Simulations demonstrate the potential of OP-based genetic mapping for identifying QTL in apples, reducing the logistical challenges associated with traditional QTL mapping methods. Our results show that OP-based genetic mapping could be used to speed up the identification of novel alleles directly from diverse germplasm collections in apples.