Unraveling the cis-regulatory code controlling abscisic acid-dependent gene expression in Arabidopsis using deep learning
Unraveling the cis-regulatory code controlling abscisic acid-dependent gene expression in Arabidopsis using deep learning
Opdebeeck, H.; Smet, D.; Thierens, S.; Minne, M.; De Beukelaer, H.; Zuallaert, J.; Van Bel, M.; Van Montagu, M.; Degroeve, S.; De Rybel, B.; Vandepoele, K.
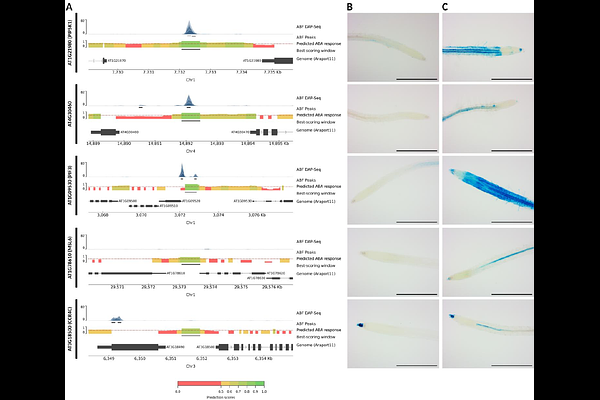
AbstractAbscisic acid (ABA) is a key regulator of abiotic stress responses in plants. Understanding the regulation of ABA-dependent gene expression is key to uncovering how plants adapt to environmental stress and how their resilience can be improved. We explored gene expression regulation by ABA in Arabidopsis thaliana through the training of an interpretable deep learning model predicting ABA responsiveness in the root from proximal promoter sequences. Implementing state-of-the-art augmentation strategies to boost performance, our convolutional neural network-based model was able to confidently predict ABA responsiveness. We demonstrate that it learned actual motifs in the promoter sequences and confirm that ABRE-binding factor (ABF) binding sites play a key role in regulating ABA-dependent gene expression. However, also other motifs contributing to ABA-mediated gene expression regulation were identified. Our model outperforms a model trained to predict ABF binding, indicating it successfully learned the cis-regulatory code beyond the canonical ABF binding sites. Furthermore, the importance of motif clustering for regulating gene expression levels in response to ABA was unveiled by our model. Lastly, we identified genomic regions, beyond the proximal promoter, both with and without ABF binding sites, predicted by our model to drive ABA responsiveness. These genomic regions were used to generate reporter lines for experimental validation and were shown to drive the response to ABA in planta. This confirms that our model successfully inferred the regulatory code controlling ABA-dependent gene expression.