APOE4 homozygotes have less sleep fragmentation in late adulthood
APOE4 homozygotes have less sleep fragmentation in late adulthood
Cho, G.; Chen, A.; Choi, E.; Buxton, O.; Kay, D.; Miner, B.
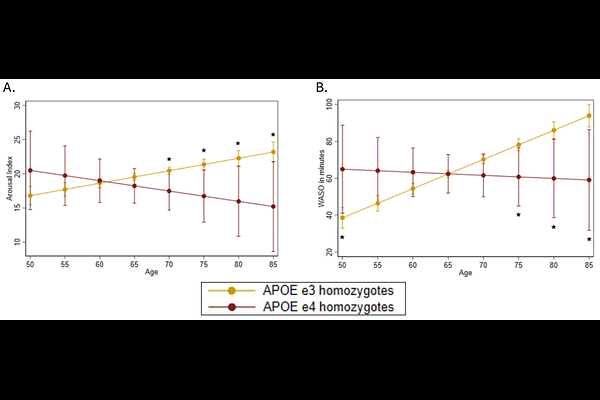
AbstractStudy objectives The presence of APOE4, a genetic risk factor for Alzheimers Disease (AD), is associated with reduced functional connectivity of brain regions that regulate sleep, which may predispose persons to AD via altered sleep architecture. However, little is known about differences in sleep architecture by APOE genotype, and whether they vary by age and sex. Methods This cross-sectional study examined the association between APOE genotype and sleep architecture, using in-home polysomnography (Sleep Heart Health Study, N=3,107). APOE genotype included: APOE4 heterozygotes, APOE4 homozygotes, APOE2 carriers, and APOE3 homozygotes (reference). Sleep architecture was quantified using the percentage of time spent in rapid eye movement sleep (%REM), N1 (N1%), N2 (%N2), N3 (%N3), and arousal index. Linear regression was employed, adjusting for age, sex, marital status, race, education, and parent cohort. Interactions with age and sex-stratified analyses examined variations by age and sex, respectively. Results The median age was 67 years, 27.4% carried at least one APOE4 allele, and 52.9% were females. Without age by APOE genotype interaction, %REM, %N1, %N2, %N3, and arousal index were comparable across APOE genotypes in the full sample, males, and females. When an age by APOE genotype interaction was introduced, APOE4 homozygotes showed fewer arousals with each year of age (beta=-0.33 arousals, p=0.04), leading to significantly less arousals at age >=70 (marginal difference=-2.98, p=0.04). Conclusions Compared with APOE3 homozygotes, APOE4 homozygotes showed comparable proportions of REM, N1, N2, and N3, but exhibited fewer arousals in old age. APOE4 homozygotes may have an elevated arousal threshold. Key words Sleep architecture, APOE genotype, Alzheimers disease, sleep fragmentation, arousals, wake after sleep onset