Prevention and reversal of hypertension-induced coronary microvascular dysfunction by a plant-based diet
Prevention and reversal of hypertension-induced coronary microvascular dysfunction by a plant-based diet
Najjar, R. S.; Hekmatyar, K.; Wang, Y.; Ngo, V. L.; Lail, H.; Tejada, J. P.; Danh, J. P.; Wanders, D.; Feresin, R. G.; Mehta, P. K.; Gewirtz, A.
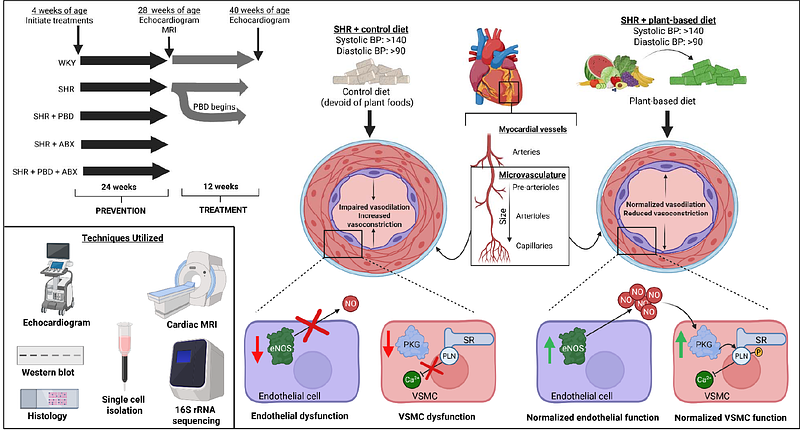
AbstractBackground and aims: Coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD) is associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes. CMD is driven by endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) dysfunction. We aimed to test whether CMD could be mitigated by a plant-based diet (PBD) in an animal model of hypertension. Methods: We compared 28- and 40-week-old female normotensive Wistar-Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats, maintained, from age 4 weeks, on a control refined diet or a PBD, comprised of 28% fruits, vegetables, nuts and legumes. A subset of control SHRs were switched to the PBD at 28 weeks. CMD was assessed by coronary flow reserve via echocardiogram. Cardiac microvascular endothelial function was assessed via cMRI. Endothelial and VSMC function were assessed in the left ventricle (LV) or in isolated VSMCs. The role of gut microbiota was probed via 16S sequencing and antibiotics. Cardiac inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis were also explored. Results: SHRs had endothelial and VSMC dysfunction. PBD did not ameliorate their hypertension but, nonetheless, prevented and reversed CMD. PBD\'s mitigation of CMD was associated with improved endothelial nitric oxide synthase function and NO-mediated VSMC signaling, as well as reductions in LV oxidative stress, inflammatory signaling, and fibrosis. PBD altered the gut microbiota, although antibiotic studies failed to establish its importance in ameliorating CMD. Conclusions: A PBD prevented CMD development and reversed established CMD in SHRs. Such benefits of PBD, which occurred without alleviating hypertension, were likely due to improved endothelial and VSMC function. These results support clinical trials to test PBDs in human CMD.