Off-Target Structural Insights: ArnA and AcrB in Bacterial Membrane Protein Cryo-EM Analysis
Off-Target Structural Insights: ArnA and AcrB in Bacterial Membrane Protein Cryo-EM Analysis
Caliseki, M.; Borucu, U.; Yadav, S.; Schaffitzel, C.; Kabasakal, B. V.
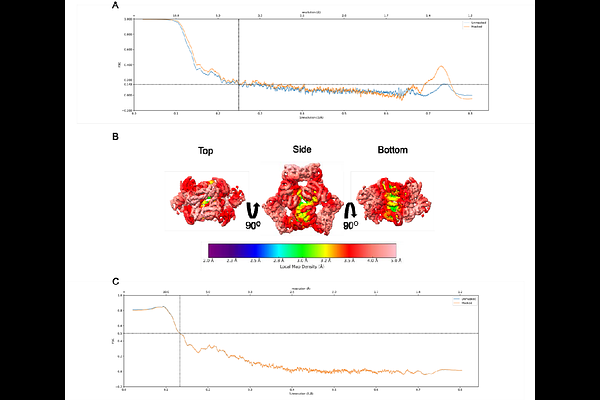
AbstractMembrane protein quality control in Escherichia coli involves coordinated actions of the AAA+ protease FtsH, the insertase YidC, and the regulatory complex HflKC. These systems maintain proteostasis by facilitating membrane protein insertion, folding, and degradation. To gain structural insights into a putative complex formed by FtsH and YidC, we performed single-particle cryogenic electron microscopy on detergent-solubilized membrane samples, from which FtsH and YidC were purified using Ni-NTA affinity and size exclusion chromatography. Although SDS-PAGE analysis indicated a high purity of these proteins, cryo-EM datasets unexpectedly yielded high-resolution structures of ArnA and AcrB at 4.0 [A] and 2.9 [A] resolutions, respectively. ArnA is a bifunctional enzyme involved in lipid A modification and polymyxin resistance, while AcrB is a multidrug efflux transporter of the AcrAB-TolC system. ArnA and AcrB are known membrane protein contaminants after Ni-NTA purifications. However, they were also detected in Strep-Tactin affinity purified FtsH-YidC samples. ArnA, typically cytoplasmic, was consistently found in membrane-isolated samples, indicating an association with membrane components. Two-dimensional class averages revealed additional particles resembling GroEL, cytochrome bo oxidase, and the AAA+ cytoplasmic domain of FtsH. Although our preparation was initially considered homogeneous, neither full-size FtsH nor the intact FtsH-YidC complex could be resolved. This case highlights that cryo-EM can reveal structural information beyond the intended target, and that overexpression of membrane proteins involved in quality control may lead to the co-purification of proteins such as ArnA and AcrB.