Cytokine profiling identifies circulating IL-2, IL23 and sPD-L1 as prognostic biomarkers for treatment outcomes in Non-Small cell Lung Cancer patients undergoing anti-PD1 therapy
Cytokine profiling identifies circulating IL-2, IL23 and sPD-L1 as prognostic biomarkers for treatment outcomes in Non-Small cell Lung Cancer patients undergoing anti-PD1 therapy
Jain, K.; Goel, A.; Mehra, D.; Rathore, D. K.; Binayke, A.; Aggarwal, S.; Ganguly, S.; Awasthi, A.; MADAN, D. E.; Ganguly, N. K.
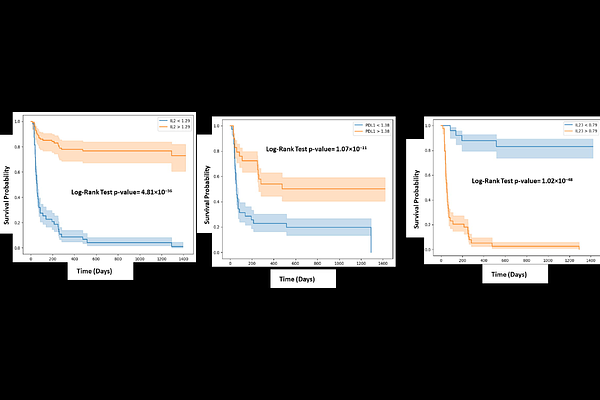
AbstractBackground: This study investigates the predictive potential of circulating cytokines for response and survival outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. Materials and Methods: A cohort of 64 patients with advanced NSCLC receiving ICI therapy were included. Baseline serum samples were collected prior to ICI initiation and profiled using a multiplex cytokine panel. Logistic regression, Cox regression, and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis were employed to assess associations between cytokine levels, therapeutic response, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Gene expression levels of key cytokines were validated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) using quantitative real-time PCR. Results: Elevated baseline levels of IL-2, IL-23, and sPD-L1 were significantly associated with clinical response to ICI therapy. Among these, sPD-L1 emerged as an independent predictor of response (AUC = 0.87). Multivariate Cox regression showed IL-2 (HR = 0.67), sPD-L1 (HR = 0.15), and IL-23 (HR = 1.18) were significantly associated with PFS and also predictive of OS. Notably, combined profiling of IL-2 and sPD-L1 enhanced predictive power (AUC = 0.95 for both PFS and OS). RT-PCR analysis of PBMCs corroborated these findings, confirming upregulation of IL-2 in responders and elevated IL-23 expression in non-responders. Conclusion: Baseline cytokine profiling, particularly of IL-2, sPD-L1, and IL-23 provides important prognostic and predictive information in advanced NSCLC patients undergoing ICI therapy. These biomarkers may facilitate more personalized approaches to immunotherapy and guide clinical decision-making.