Reference-guided genome assembly at scale using ultra-low-coverage high-fidelity long-reads with HiFiCCL
Reference-guided genome assembly at scale using ultra-low-coverage high-fidelity long-reads with HiFiCCL
Jiang, Z.; Pan, W.; Gao, R.; Hu, H.; Gao, W.; Zhou, M.; Yin, Y.-H.; Qian, Z.; Jin, S.; Wang, G.
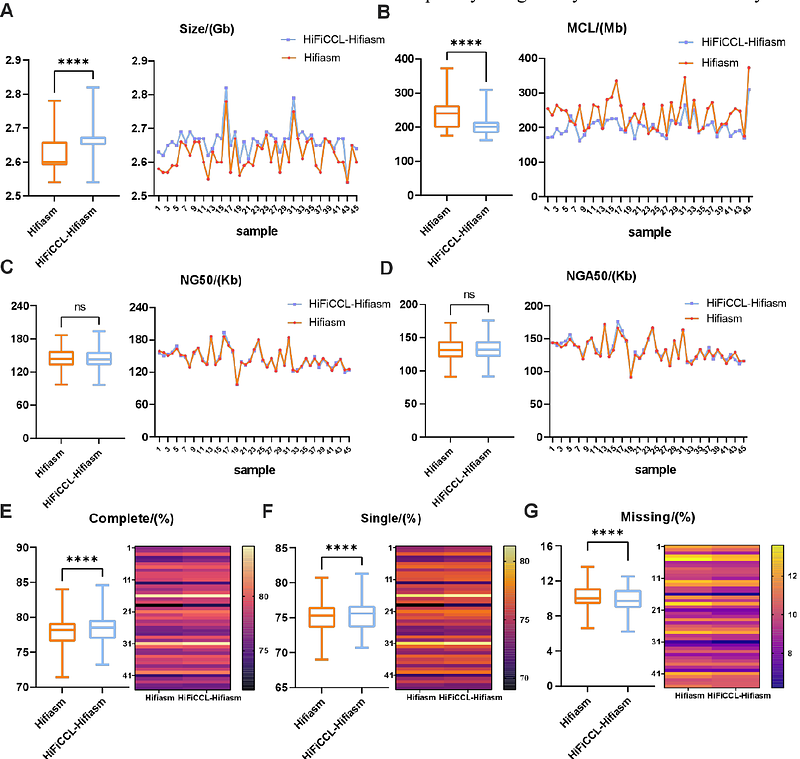
AbstractPopulation genomics using short-read resequencing captures single nucleotide polymorphisms and small insertions and deletions but struggles with structural variants (SVs), leading to a loss of heritability in genome-wide association studies. In recent years, long-read sequencing has improved pangenome construction for key eukaryotic species, addressing this issue to some extent. Sufficient-coverage high-fidelity (HiFi) data for population genomics is often prohibitively expensive, limiting its use in large-scale populations and broader eukaryotic species and creating an urgent need for robust ultra-low coverage assemblies. However, current assemblers underperform in such conditions. To address this, we propose HiFiCCL, the first assembly framework specifically designed for ultra-low-coverage high-fidelity reads, using a reference-guided, chromosome-by-chromosome assembly approach. We demonstrate that HiFiCCL improves ultra-low-coverage assembly performance of existing assemblers and outperforms the state-of-the-art assemblers on human and plant datasets. Tested on 45 human datasets (~5x coverage), HiFiCCL combined with hifiasm reduces the length of misassembled contigs relative to hifiasm by an average of 21.19% and up to 38.58%. These improved assemblies enhance germline structural variant detection, reduce chromosome-level mis-scaffolding, enable more accurate pangenome graph construction, and improve the detection of rare and somatic structural variants based on the pangenome graph under ultra-low-coverage conditions.