Integrative cross-sample alignment and spatially differential gene analysis for spatial transcriptomics
Integrative cross-sample alignment and spatially differential gene analysis for spatial transcriptomics
Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, A.; Yan, Y.; Lin, W.; Nie, Q.; Shi, J.
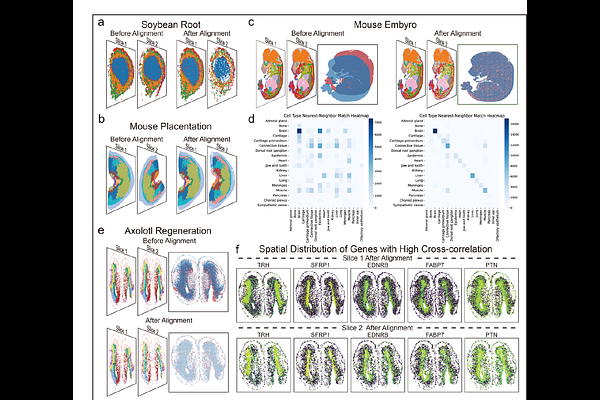
AbstractSpatial transcriptomics (ST) technologies offer rich spatial context for gene expression, with varying spatial resolutions and gene coverages. However, aligning and comparing multiple ST slices, whether derived from the same or different platforms, remains challenging due to nonlinear distortions and limited spatial overlap caused by tissue processing. We present CODA, an integrative framework for CrOss-sample alignment and spatially Differential gene Analysis. CODA first learns a shared low-dimensional latent feature space across samples. Within the latent space, CODA performs global rigid alignment, applies transformer-based feature matching to identify common spatial domains, and utilizes local nonlinear refinements via large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping, enabling a robust cross-sample comparison and extraction of spatial gene expression patterns. Benchmarking across various ST platforms demonstrates that CODA outperforms the existing methods in alignment accuracy, computational efficiency, and memory usage. Applications to vascular and brain datasets shows CODA\'s ability to uncover spatially informative genes associated with disease and sleep regulation. These results highlight CODA\'s broad applicability and effectiveness in ST analysis.