Chorionic Gonadotropin Beta 7 is a marker of immune evasion in cancer
Chorionic Gonadotropin Beta 7 is a marker of immune evasion in cancer
McKellar, S. A.; Pineda, J. M. B.; Lattupally, R.; Codd, A. S.; Newell, E.; Lu, S. X.; Bradley, R. K.
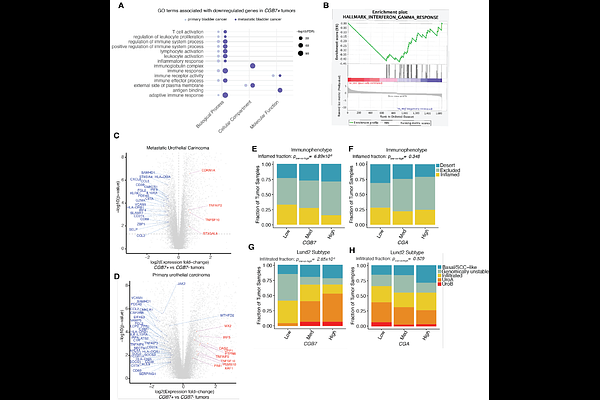
AbstractHuman chorionic gonadotropin beta (beta-hCG) is an oncofetal antigen expressed by trophoblast cells of the placenta, with minimal expression in adult somatic tissues. Numerous studies have demonstrated that beta-hCG-encoding genes are expressed in various cancers, but expression of these genes (CGB3, CGB5, CGB7, and CGB8) across diverse cancers has not been systematically evaluated. Here, we report that CGB genes are more widely expressed across diverse cancer types than previously appreciated and that secreted beta-hCG is readily detected. In particular, CGB genes are expressed in the majority of urothelial bladder cancers, where CGB7 is most frequently expressed and significantly associated with an immunosuppressed tumor microenvironment, including decreased CD8+ T cell infiltration. Multiple CGB genes are associated with failure to respond to immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, and CGB7 is particularly strongly predictive of poor prognosis. Overall, our findings indicate that beta-hCG is a clinically accessible, predictive biomarker of immunotherapeutic response.