Transcriptomic insights into early diagnosis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in a rat model
Transcriptomic insights into early diagnosis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in a rat model
Anca, E.; Pavel, I. O.; Licarete, E.; Rosioru, C.; Dobre, C.; Banciu, M.
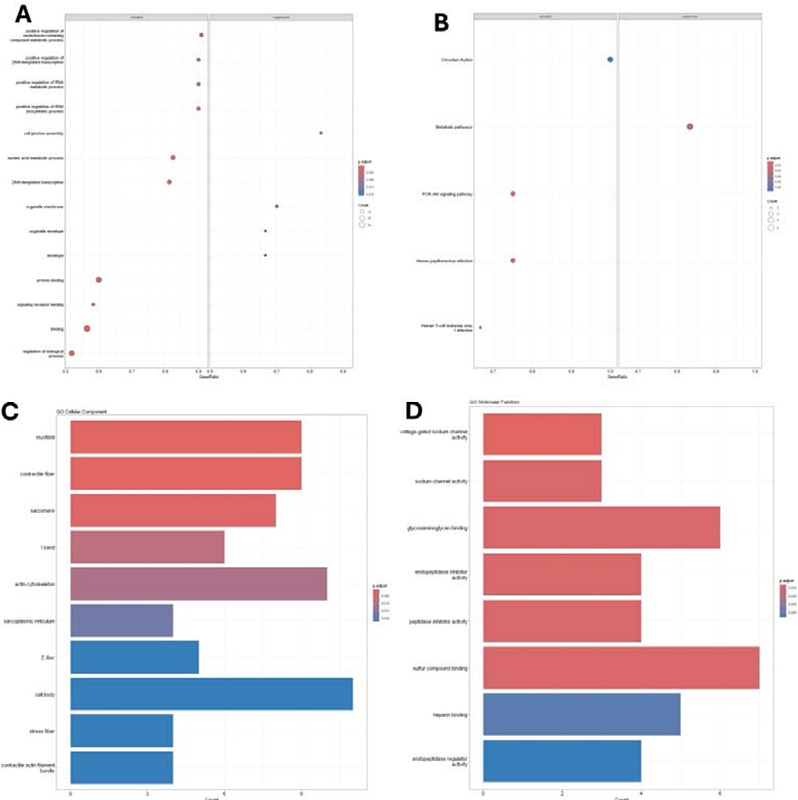
AbstractDoxorubicin is a member of the anthracycline class of chemotherapeutic agents and is among the most effective treatments available up to date. However, its clinical use is significantly limited by severe cardiotoxic effects. The purpose of this study is to investigate the transcriptomic alterations that occur in a rat model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Our results reveal significant dysregulations of cardiac metabolism and provide insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying cardiac damage produced by this treatment. Our analysis revealed that heart tissue recovery following doxorubicin treatment is hindered by hypercholesterolemia exacerbated by transcriptomic-level alteration of the circadian rhythm. This result could help facilitate the discovery of circulating biomarker-based early diagnostic methods for this disease, along with cardioprotective treatment implementation.