Determination of chemical partitioning in vehicles using a skin surrogate for dermal absorption model refinement.
Determination of chemical partitioning in vehicles using a skin surrogate for dermal absorption model refinement.
Pendlington, R.; Sanders, D.; Sheffield, D.; Glavin, S. E.; Barlow, H. J.; Li, H.
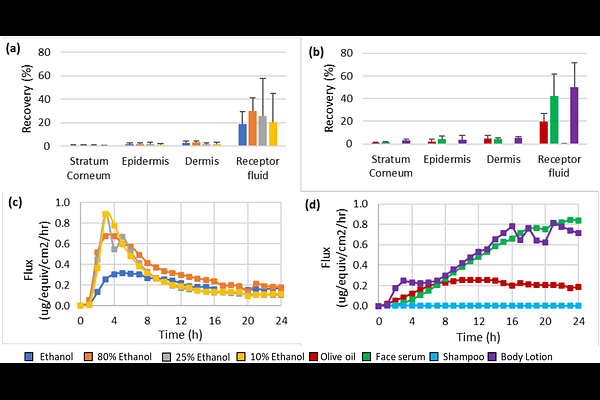
AbstractIn nonclinical safety assessments of cosmetic ingredients applied topically, it is essential to investigate the rate and extent of dermal penetration to reach the systemic circulation. The initial step in skin absorption involves the partitioning of an ingredient from the formulation into the upper layer of the stratum corneum and this plays a key role in determining the delivery of an ingredient. Currently, there is a lack of reliable methods to accurately predict this important parameter. To address this, we measured the partitioning of three chemicals from seven different vehicles into a surrogate PDMS membrane; these measurements were then used to parameterize a dermal absorption model. The evaluation of receptor fluid kinetics and skin absorption percentages, comparing measured and predicted data, demonstrated that incorporating the vehicle partitioning parameter derived from the PDMS system improved the accuracy of model predictions for the three chemicals in most vehicles.