SOX2 and SOX9 as Transcriptional Regulators of human Galectin-3 in SW1353 Cells: Potential Implications for Osteoarthritis
SOX2 and SOX9 as Transcriptional Regulators of human Galectin-3 in SW1353 Cells: Potential Implications for Osteoarthritis
Alba, B.; Schmidt, S.; Kaltner, H.; Toegel, S.
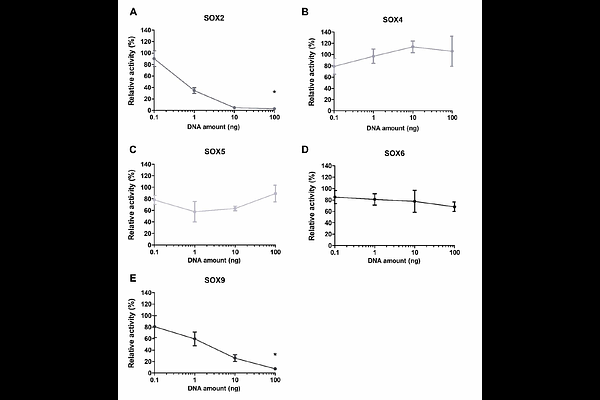
AbstractGalectin-3 (Gal-3), a member of the {beta}-galactoside-binding protein family, is critically involved in inflammation, extracellular matrix remodelling, and cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis (OA). This study aims to elucidate the regulation of the human galectin-3 gene (LGALS3) promoter in SW1353 cells and its control by SOX transcription factors, known to be dysregulated during OA pathogenesis. We sought to identify key sequence elements in the LGALS3 promoter responsible for its transcriptional activity and the transcription factors (TFs) responsible for its regulation. Using luciferase reporter assays, we examined deletion variants of the 5\' region (-2638 bp to +52 bp) and assessed their activation potential. We also identified potential transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) through in silico analyses and confirmed SOX9 binding in the -93/+49 region by chromatin immunoprecipitation using HaloCHIPTM. Functional assays revealed that the proximal promoter region (-97 to +52 bp) is critical for reporter gene expression in SW1353 cells. This study demonstrates that the presence of SOX2 and SOX9 leads to a dose-dependent decrease in LGALS3 promoter activity in SW1353 cells. We show that SOX9 can bind the promoter, highlighting the importance of SOX TF interactions in regulating LGALS3 expression and their potential role in chondrocytes.