Repurposing Romidepsin for Osteosarcoma: Screening FDA-Approved Oncology Drugs with Three-Dimensional Osteosarcoma Spheroids
Repurposing Romidepsin for Osteosarcoma: Screening FDA-Approved Oncology Drugs with Three-Dimensional Osteosarcoma Spheroids
Seiden, E. E.; Richardson, S.; Everitt, L. A.; Knafler, G. J.; Kinsella, G. P.; Walker, A. L.; Whiteside, V. A.; Buschbach, J. D.; Gandhi, D. A.; Saadatzadeh, M. R.; Wurtz, L. D.; Getty, P. J.; Padgett, S. L.; Gamblin, R. M.; Childress, M. O.; Fulkerson, C. M.; Pollok, K. E.; Collier, C. D.; Greenfield, E. M.
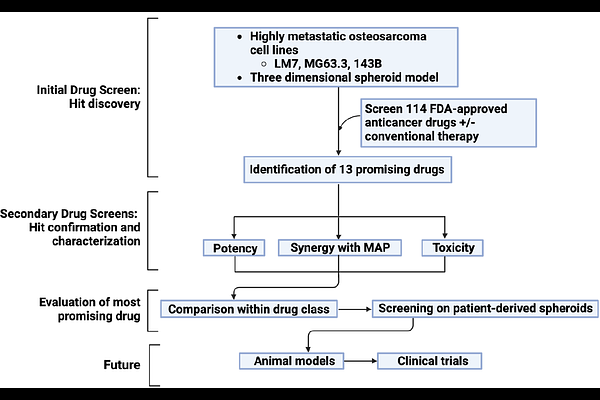
AbstractOsteosarcoma is the most common primary malignant bone tumor and predominantly affects children, adolescents, and young adults. It is the third most common cause of cancer-related deaths among 9-24-year-olds. Despite aggressive chemotherapeutic and surgical therapies, the survival rate is only 25% for patients with detectable lung metastases at diagnosis and only 70% in patients that present without detectable lung metastases. The poor prognosis is due to growth of metastases irrespective of whether they are initially large enough to detect clinically. It is therefore necessary to develop new methods to target the growth of lung micrometastases. An NCI panel of FDA approved oncology drugs was therefore screened using three highly metastatic human osteosarcoma cell lines. To more closely approximate in vivo micro-metastases, the screen used a 3D multicellular in vitro osteosarcoma spheroid (sarcosphere) model. Among 13 hits from the initial screen, we identified the histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDI) romidepsin as the most promising inhibitor in secondary screens based on sarcosphere viability. Romidepsin potency was evident with and without standard-of-care chemotherapeutics (MAP: Methotrexate, Adriamycin, Cisplatin) at drug concentrations that are clinically achievable and did not affect non-transformed cells. By those criteria, romidepsin also substantially outperformed the other three FDA approved HDIs and eight HDIs in clinical trials. Importantly, sarcospheres derived at low-passage number from 30-50% of human and canine patient samples were also sensitive to romidepsin with ED50s 10- to 700-fold less than the Cmax in human patients. Based on these 3-D screening approaches, romidepsin is a promising drug to repurpose for osteosarcoma. The next most promising FDA-approved drugs were bortezomib and carfilzomib, the only two proteosome inhibitors in the NCI panel.