Metabolic Reprogramming of Pathogenic CD4+ T Helper Cells Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis
Metabolic Reprogramming of Pathogenic CD4+ T Helper Cells Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis
Mishra, S. K.; Abdelrahman, L. M.; Davidson, H. M.; Kim Lee, H. S.; Valenzuela-Perez, L.; Hassan, O. M.; Faubion, W. A.; Hirsova, P.; Bamidele, A. O.
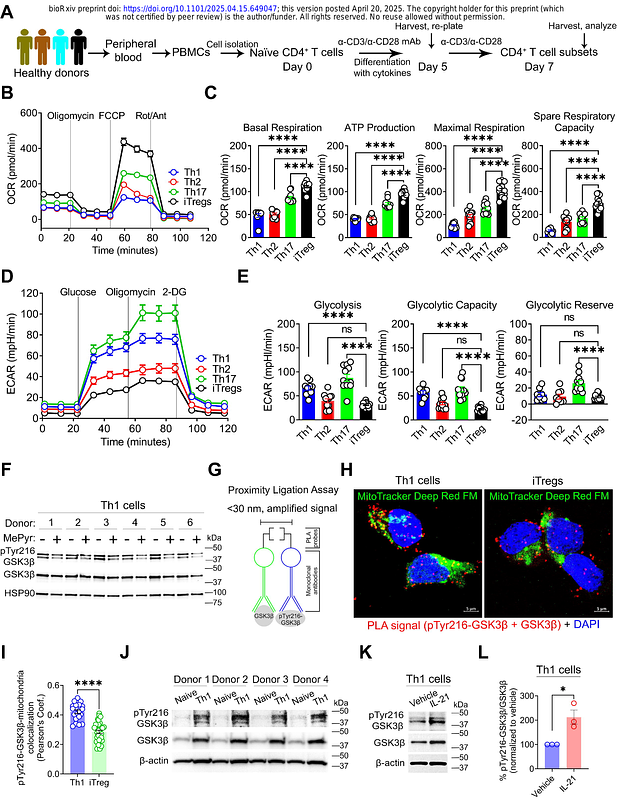
AbstractBACKGROUND & AIMS: CD4+ T helper 1 (Th1) cells are involved in human inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) pathogenesis; however, mechanisms governing the persistent inflammatory function of these cells are unclear, leading us to examine how metabolism governs Th1 cell-induced IBD. METHODS: Th1 cells supplemented with methyl pyruvate (MePyr) were analyzed to define how enforced mitochondrial pyruvate metabolism and subsequent glycogen synthase kinase 3{beta} (GSK3{beta}) deactivation reprogram cellular state. Re-analysis of the inflamed ileal single-cell RNA sequencing dataset from Crohn\'s disease patients was performed to assess non-Treg CD4+ T cell metabolic gene signature. We assessed the capacity of a repurposed GSK3{beta} inhibitor to restrain pathogenic CD4+ T cell-driven murine colitis. RESULTS: Effector Th1 cells exhibit a distinct metabolic program exemplified by glucose-driven glycolysis but low mitochondrial respiration. MePyr deactivates GSK3{beta}, glycolysis, and histone H3 acetylation on cytokine promoter region, resulting in reduced interferon-{gamma} (IFN-{gamma}) and tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) expression in Th1 cells with concomitant gain of regulatory T cell-like program. GSK3{beta} inhibition with LY2090314 mirrored the anti-inflammatory effect of MePyr in a manner reversible by acetate supplementation, implying that GSK3{beta} potentially sustains glycolysis-derived acetyl-coenzyme A needed for histone acetylation and Th1 cell inflammatory response. Interleukin-21 exacerbates Th1 cell inflammatory response by maintaining a GSK3{beta}-driven glycolytic program. The Th1 cell metabolic gene signature downregulated by MePyr or GSK3{beta} inhibition in vitro is enriched in refractory Crohn\'s disease patients. GSK3{beta} inhibition with LY2090314 retrains T cell-induced colitis in mice. CONCLUSIONS: MePyr impairs GSK3{beta}-mediated glycolysis and Th1 cell immune response. GSK3{beta} inhibition may mitigate Th1 cell-induced human IBD.